What is an APT Attack?
APT attacks, small for advanced persistent threats, are a type of cyberattack where threat actors get access to an organization’s network and successfully remain undetected for an extended period. The period can vary from a year to five years.
Table of Contents
ToggleThese attacks are very well-planned for a specific organization to evade its security measures without alerting security officers.
On average, enterprises experience 130 security breaches per year per organization.
Advanced persistent threats may have the below-mentioned characteristics:
- The general presence of backdoor Trojans.
- Unusual folders of data at the uncommon location, implementing data has been gathered to be tempered with.
- Uncommon login activity, especially at off-hours of the organization.
- Unexplained data operation and data outflow.
Knowing what are advanced persistent threats, it’s also critical to be aware of the different stages of APT attacks.
Stages of Advanced Persistent Threats
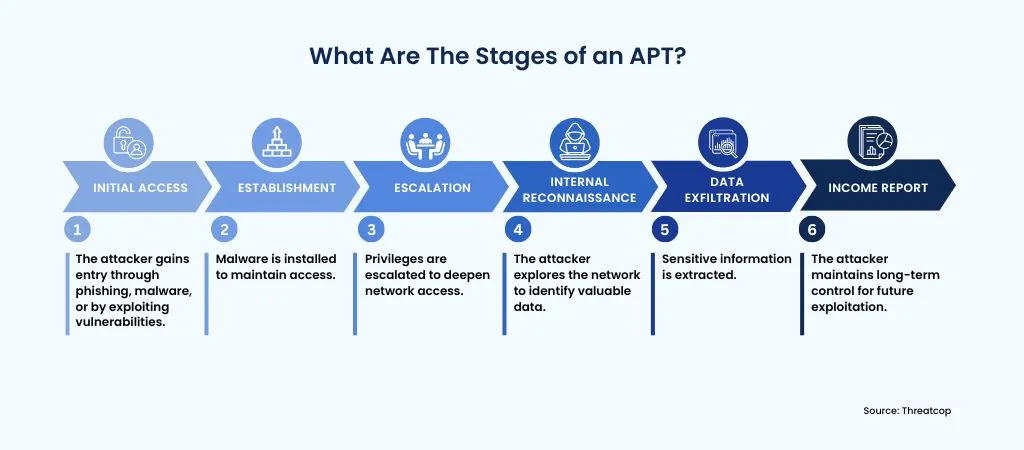
For a successful APT attack, the cybercriminal has to go through the three main stages, too, without getting noticed.
Stage 1: Infiltration
To begin with, the threat actor gains access to the organization’s network via social engineering techniques. For example, using standard spear phishing method, i.e. common threat received by employees regularly.
Stage 2: Expansion
Once the access is gained, the cyber criminals proceed to move up the hierarchy, targeting high-level executives who have access to the company’s sensitive data.
The data gained is used in different ways, depending on the goal. It can be sold to competitors, alter or disturb the whole product line of the company, and so on.
Stage 3: Extraction
All the information is typically stored in a safe location in the network until enough data is available. Once collected, cybercriminals plan to extract without getting caught. To play it safe, they often disturb the network and display a DoS attack (Denial of Service) to extract successfully.
In 2020, A Chinese-state-sponsored group, ATP41, targeted multiple industries across the world for money laundering, identity theft, and racketeering. The group allegedly had unauthorized access to protected computers to steal sensitive information. The victims were from across the world, mainly Brazil, Germany, India, Australia, and so on. The defendants allegedly deployed ransomware attacks and demanded payments from victims.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
How to Detect an ATP Attack?
– Selected Executives Receiving Phishing Emails
ATP groups often target high-level company leaders and send phishing emails using the attached PDF. The PDFs, when opened, launch malicious software, making their attempt successful.
– Data Moved to an Unusual Location
Before extraction, such a group moves data to a single secure place in the network. If you find a large volume of critical data in compressed form in a single place, it’s likely to be an ATP attack.
– Uncommon Logins to User Accounts
ATP group acts in different time zones and, therefore, logs in to the systems at off-timing. If you observe some late-night login activity in your systems, it’s time to be alert for ATP attacks.
With the basic knowledge of what are advanced persistent threats, the employees of an organization are one step closer to detecting fraudulent activities.
Proactive Measure Against ATP Attack
Hackers often keep backdoors open even after they are discovered. This allows them to return whenever they wish to, making the ATP attack highly dangerous. Even antivirus and firewalls are not 100% successful in protecting and identifying such attacks.
The best bet to protect your system against the attack is to train every person in your organization’s network. Keeping employees aware and trained about APT threats and other social engineering attacks will less likely lead them to click on suspicious emails and links.
78% of employees are aware of the risks of suspicious links in emails but click on them anyway
An organization’s CISO responsibility is to make training fun and entertaining enough to be preferred by employees. Also, a simulator that checks vulnerabilities in the organization can be a proactive measure. TSAT, a cyber-attack simulator and training solution, aims to promote a sense of security awareness in the organization. The tool also introduces employees to newly modeled vulnerabilities via interactive content of cyber threats, such as phishing, smishing, WhatsApp, and more.
Related:
Co-Founder & COO at Threatcop
Department: Operations and Marketing
Dip Jung Thapa, Chief Operating Officer (COO) of Threatcop, a leading cybersecurity company dedicated to enhancing people security management for businesses. With a profound understanding of cybersecurity issues, Dip plays a pivotal role in driving Threatcop’s mission to safeguard people’s digital lives.
Co-Founder & COO at Threatcop Department: Operations and Marketing Dip Jung Thapa, Chief Operating Officer (COO) of Threatcop, a leading cybersecurity company dedicated to enhancing people security management for businesses. With a profound understanding of cybersecurity issues, Dip plays a pivotal role in driving Threatcop's mission to safeguard people's digital lives.
