Fraudsters can take advantage of human vulnerabilities through email impersonation attack. Impersonation attacks have infinite variations and each one depends on the target’s quick reaction to emails and misguided trust in surface appearance. Both people and brand impersonation can be difficult to detect. This is difficult only in a lack of security awareness.
Table of Contents
ToggleSubscribe to Our Newsletter On Linkedin
Sign up to Stay Tuned with the Latest Cyber Security News and Updates
What are Email Impersonation Attack?
In an email impersonation attack, scammers create fraudulent emails and disguise themselves as a trusted entity or someone from higher authorities in the organization. These scammers mainly target employees of an organization as they are the most vulnerable asset. Attackers trick employees into transferring sensitive data or revealing login credentials for malicious purposes.
A few examples of email impersonation attacks are pretending to be the CEO of the company, coming from a government authority, and someone from the high authority of an organization. The primary step to mitigate email impersonation attacks is to have strong email security standards, password policies, and security awareness training for people. If you are unsure if the email is legitimate, remember don’t click on it. Until and unless you are sure that it is safe.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
How do Email Impersonation Attack Work?
It is a form of BEC attack to impersonate someone via email that uses social engineering attack techniques to gain the target’s trust. Email Impersonation attacks can take the form of spoofing or account takeover. Attackers steal login credentials to access an email account to send phishing emails and steal data. Threat actors conduct extensive research on their target using various sources. By misusing the researched information of their targets, these threat actors pretend legitimate to be entities and give credibility to their message.
Typically, scammers target individuals of an organization, who can transfer funds or access proprietary information. Once the attacker has the information, they attempt to create bogus emails. These emails appear to be sent by high-level executives and are designed to trick victims into sending money or sensitive information.
Statistics on Email Impersonation Attack (2022)
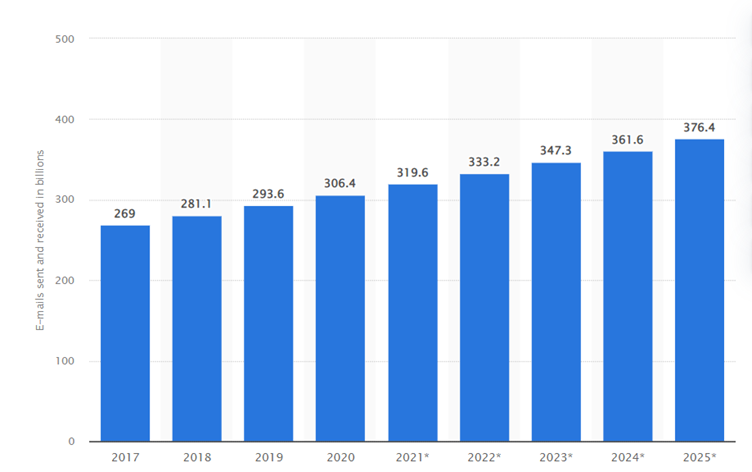
Cybercriminals have long used phishing as a tactic to steal from their victims. It usually happens via email, with scammers posing as trusted individuals or organizations to dupe unsuspecting victims into divulging sensitive information. While the year 2022 is not yet over, scammers have already launched several attacks.
#1 Nearly 70% of scam emails have an empty ‘subject’ line
An unused subject line is a tell-tale indication that the email received is a spam email attempt. According to research, 67% of cybercriminals send malicious emails with no subject line. Other less common subject lines used by attackers have ‘Fax Delivery Report’ (9%), ‘Business Proposal Request’ (6%), ‘Request’ (4%), ‘Meeting’ (4%), ‘You have (1*) New Voice Message’ (3.5%), ‘Re: Request’ (2%), ‘Urgent Request’ (2%), and ‘Order Confirmation’ (2%).
#2 In Q1 2022, 52% of all multilateral phishing attacks were directed at users of LinkedIn
It is well known that cybercriminals attempt cyber attacks on renowned brands. To avoid detection, they spoof the email domains to make the email like it is from a known source. In the first quarter of 2022, LinkedIn became the go-to brand for cyber attackers. LinkedIn has been used in half (52%) of the world for phishing attacks, 44% to 8% happened in the previous quarter. In terms of phishing attack targets, social media brands were the first to surpass tech giants like Apple, Google, and Microsoft.
#3 Phished crypto projects include Cardano, Luno, and Blockchain.com
Cybercriminals usually scam cryptocurrency brands for large-scale data breaches even though the cryptocurrency market has been going down. They create a fraudulent website that looks genuine to steal sensitive information. Cardano, Luno, and Blockchain.com are common brands that get phished frequently by scammers.
A cryptocurrency financial services company named Blockchain.com was the most spoofed crypto brand. They have had 662 phishing websites in the last 90 days (till June 22, 2022). A cryptocurrency investing app Luno comes in the second spot with 277 phishing websites. Followed by a proof-of-stake blockchain platform Cardano with 191 websites.
#4 Amazon Prime Day is targeted by 900 phishing sites
Amazon Prime Day has become a much-anticipated deals day for customers. While customers are enjoying it, cybercriminals are working hard to lure them into fraudulent websites. In the last 90 days (till July 12. 2022) around 1,633 suspicious sites were detected, and Amazon is the most frequent brand to be impersonated. The websites are constantly being taken down, but as of July 12, as many as 897 were still online.
#5 54% of successful phishing attacks compromise customer data
While not all cyberattacks are successful, those usually have catastrophic consequences for both organizations and their clients. According to the Atlas VPN team’s data, more than half (54%) of successful phishing attacks result in a customer or client data breach, with credential and account compromise coming in second (48%). In 2021, 83% of organizations said they had been the victim of a successful phishing attack.
In addition to data and intellectual property loss (44%), malware other than ransomware (27%), reputational damage (24%), widespread network outages and downtime (22%), advanced persistent threats (18%), financial losses (17%), zero-day exploits (15%), and financial penalties or regulatory fines (11%), there are also widespread network outages and downtimes (22%).
Tips for Protection Against Email Impersonation Attack

Email impersonation is being widely used by cybercriminals to hoodwink employees into giving up confidential information, which can be easily used to gain access to an organization’s private data. With organizations all around the world becoming victims of these attacks, it has become essential to protect your company against malicious actors. So, here are a few practical cybersecurity tips for preventing email impersonation attacks:
- An organization should inculcate employee security awareness training about the predominant cyber attack tactics and essential cybersecurity practices, they can take to prevent cyber attacks.
- Implement a Phishing Incident Response Tool such as TPIR by Threatcop to empower your employees to report any suspicious-looking emails.
- Use best practices for email security in your organizations to secure your email domain against forgery. This can also defend your customers and employees against email spoofing and brand impersonation.
- Implement an email authentication tool to monitor all three email authentication protocols (DMARC, SPF, and DKIM). To complement the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
TDMARC: Ultimate Email Security Solution
TDMARC is a GCA-certified outbound email authentication monitoring and anti-spoofing tool. It is a comprehensive email security solution designed to protect your organization against email-based attacks like spoofing, BEC attack, etc.
It protects your customers and email domain against brand abuse. Moreover, TDMARC helps in boosting email engagement rates and increases email deliverability. It offers full insight into an organization’s email channel and provides domain owners with full reports about the emails sent through their domain.
This tool delivers a domain summary of up to 3 months to offer complete visibility into the fraudulent and legitimate emails sent using your organization’s domain name. It also gives you insight into the sources trying to forge or misuse your organization’s domain name.
Senior Writer
Shantanu is an accomplished content strategist and technology enthusiast at Threatcop Inc. With a knack for translating technical intricacies into reader-friendly narratives, Shantanu contributes to making cybersecurity insights both informative and enjoyable for tech enthusiasts and general audiences alike.
Senior Writer Shantanu is an accomplished content strategist and technology enthusiast at Threatcop Inc. With a knack for translating technical intricacies into reader-friendly narratives, Shantanu contributes to making cybersecurity insights both informative and enjoyable for tech enthusiasts and general audiences alike.
