The cybersecurity service industry in India has doubled from $4.3 billion to $8.5 billion from 2019 to 2021.
(Source: Fortune India)
Every organization seeks a way to protect and secure its cybersecurity infrastructure. The methodologies and concepts utilized by security analysts within organizations fall under the domain of threat hunting. Most organizations are spending huge sums of money to enhance their cybersecurity, in which threat hunting plays a crucial role. The objective of threat hunting is to install a mechanism to repel cybercriminals through automation.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Threat Hunting?
Threat hunting is a proactive approach to seeking vulnerabilities and inspecting the cybersecurity infrastructure of an organization. The objective of threat hunting is to enhance the security of the systems and hunt for malicious elements across the endpoints of the network. The procedure of threat hunting involves consistent monitoring and storing of live data of the suspicious activity in a database.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
It not only provides a proactive approach for defending the cyber security infrastructure but also allows you to assess an organization’s level of security. It also takes responsibility for executing incident response plans. Thus, a threat hunter has to be a keen analyst who has the ability to observe the indicators of threat, orient themselves in accordance with stats to develop hypotheses, take a comprehensive decision and execute all the things cohesively.
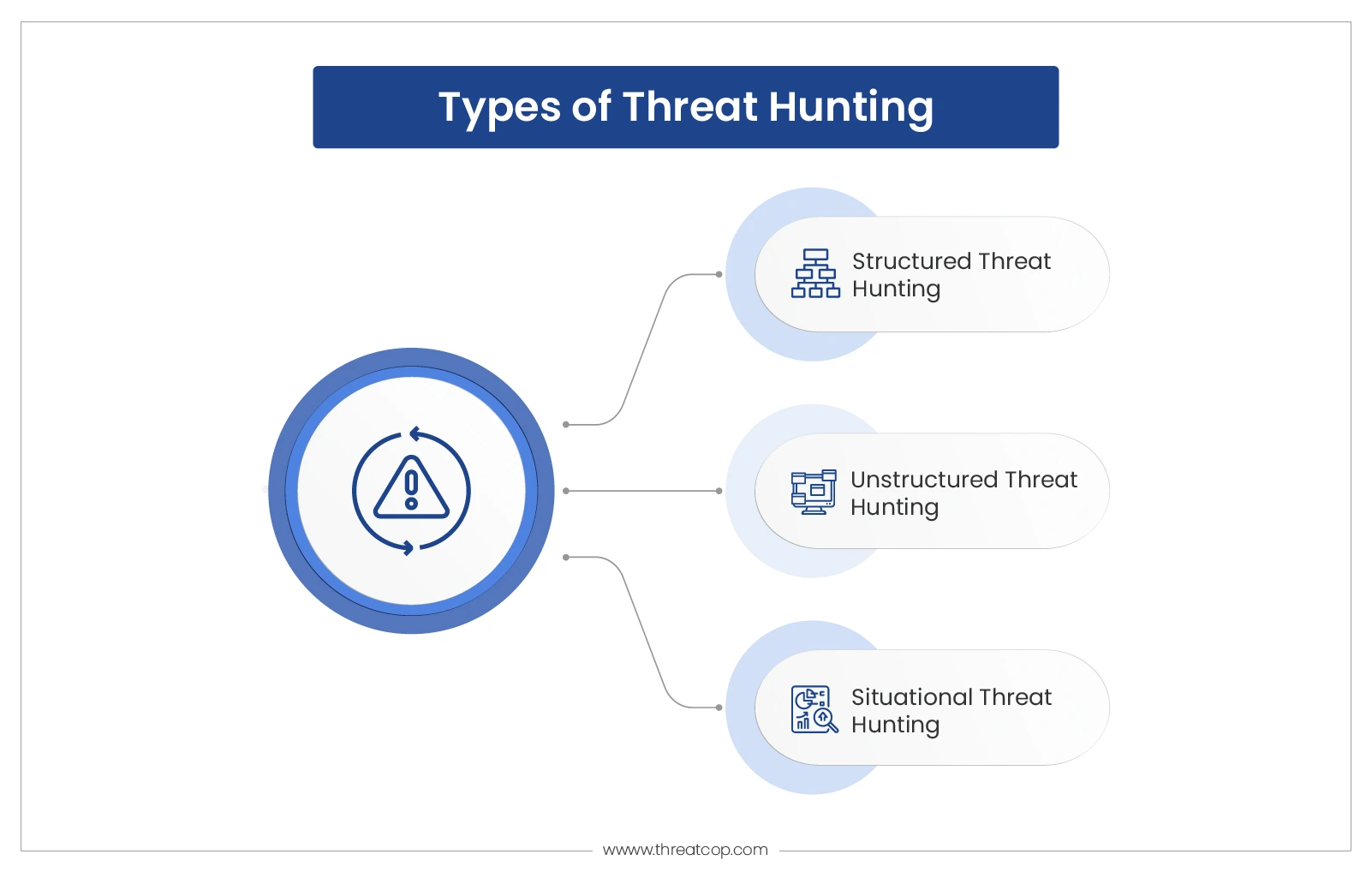
Types of Threat Hunting
Threat hunting is dependent on the framework of enterprise security that includes tools and services to secure the cyber security infrastructure of the organization. The type of threat hunting described below is based on the approach taken by the cybersecurity team. The particular approach consists of a comprehensive process of threat detection and further mitigating and resolving procedures. Threat hunting can be categorized into-
Structured Threat Hunting
Structured threat hunting is carried out by using IOAs (Indicators of Attack) to gain an understanding of techniques that could be used by attackers. The approach to this type of threat hunting is based on the methodologies previously chosen by the attackers. In other words, structured threat hunting is driven by a particular technique or methodology.
Unstructured Threat Hunting
It is primarily based on IOCs (Indicators of Compromise), whose approach is triggered. The threat hunter looks for triggers based on a particular indicator, which is devised using post- and pre-detection behavior. Unstructured threat hunting can be useful for data retention.
Situational Threat Hunting
This is an exhaustive set of procedures that is mainly based on the internal risk and vulnerabilities of the organization. This type of threat hunting involves data from assessments of previous attacks to check whether anything similar might happen again.
Methodologies for Detecting Threats
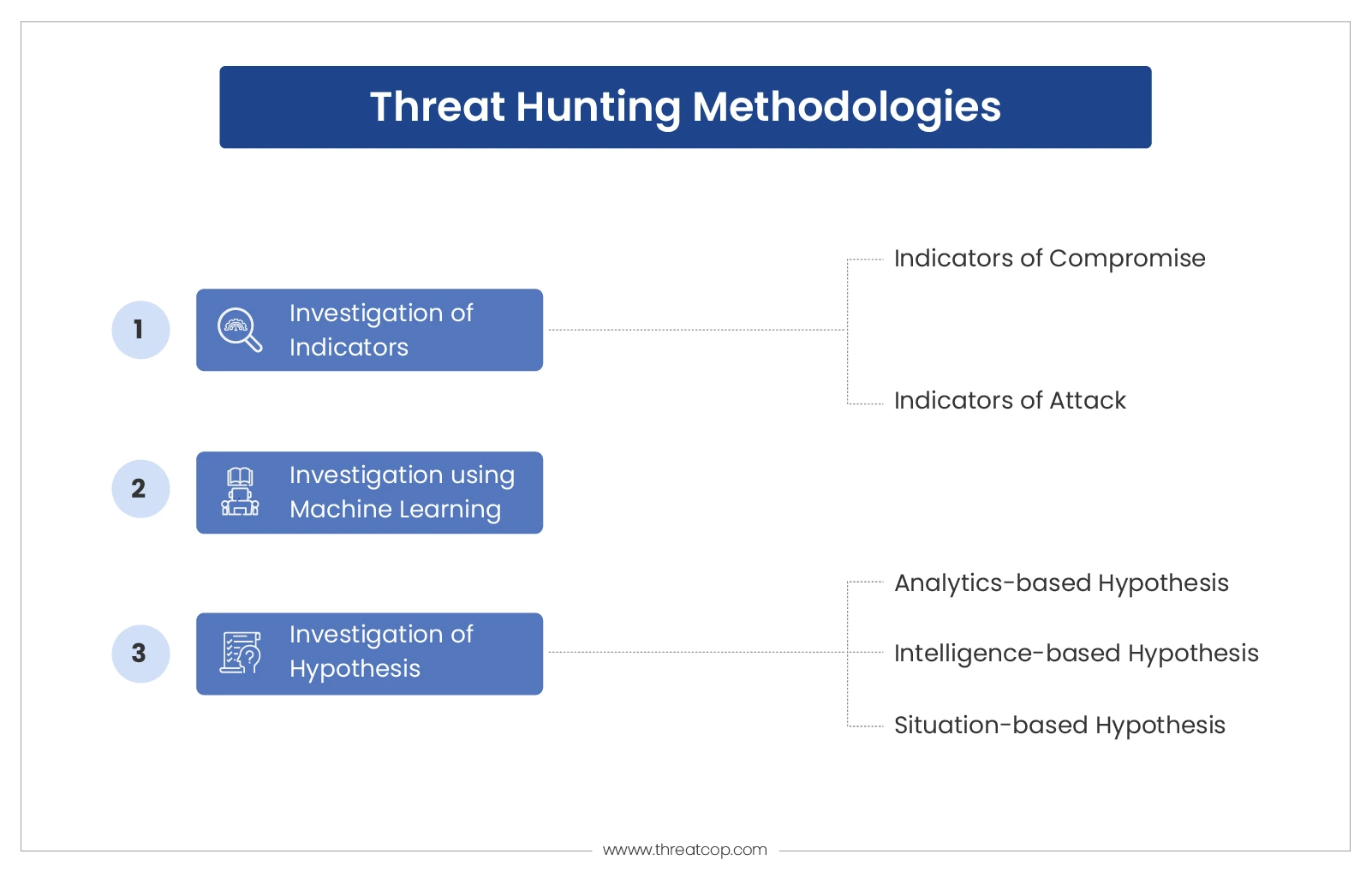
In the previous section, we discussed types of threat hunting where a collective approach was taken. Those collective approaches can be elementally divided into the following methodologies. The significance of the methodologies described below is to showcase how a particular attribute or parameter can be effectively used for threat hunting and prevention.
Investigation of Indicators
Whenever any cyber attack is carried out, it exposes loopholes in cyber security infrastructure and human intelligence. This methodology is based on a tactical approach to leverage threat intelligence. Information and collective outcomes are logged in IOCs and IOAs. Then, this catalog is used as a trigger during threat hunting. The triggers reveal the exploitation within the system or the ongoing cyber attacks.
IOCs (Indicators of Compromise)
It is a catalog that contains a set of identifications of the vulnerabilities found in the system. It is inclusive of all the vulnerabilities that have been found in that category of that particular cyber attack till date. For example, recently the Log4j library was found with vulnerabilities (log4shell) in input validation, which was updated with a patch. Furthermore, it was again found with another vulnerability, and an upgraded patch came. Such vulnerabilities become IOCs for the log4j library.
IOAs (Indicators of Attack)
IOAs differ from IOCs in a few ways. These indicators are positioned from the point of attack, which is yet to happen. In simpler words, it is a proactive approach when a vulnerability is already executed and a prevention step is taken before the threat becomes real or when a cyber attack is executed. In other words, IOAs fill the remaining gap left by IOCs during threat prevention and hunting. IOAs are responsible for alerting authorities before a cyber attack is attempted.
An Investigation Based on Hypothesis
A hypothesis is an assumption based on a certain explanation regarding a particular thing that is about to happen. In cybersecurity, there is a possibility of threat hunting through investigating a hypothesis. There are three ways in which the hypothesis can be investigated.
- Analytics-based hypothesis: There is a massive amount of data available for analysis on cyber attacks dating back to at least 20 years. This process involves the usage of data analysis concepts and machine learning algorithms to develop artificial intelligence tools for threat detection and suggesting prevention measures. The use of analytics helps in developing hypotheses consisting of UEBA (User and Entity Behaviour Analytics). UEBA is used for developing hypotheses for identifying or predicting threats based on aggregate risk scores.
- Intelligence-based hypothesis: It involves the analysis of threat vectors such as malware, email threats, phishing, viruses, worms, etc. It includes intelligence reports on risks and attack vectors that are developed by vulnerability scanning, malware analysis, phishing analysis, email analysis, etc. Using comprehensive intelligence, a hypothesis of a possible threat is predicted.
- Situation-based hypothesis: Every organization has an internal team that carries out an enterprise risk assessment, or they can hire third-party organizations to carry out VAPT (Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing) to identify possible loopholes and vulnerabilities in security.
Machine Learning or Intel-Based Investigation
The notion of “intel” in cybersecurity is said to be the source of intelligence that is gathered across networks to evaluate the parameters of security against set standards. This intelligence can be IOCs, IP addresses, domain names, hash values, etc. Considering the human-based vulnerabilities, it can also be employee assessment.
All this intelligence can be used comprehensively with previous or general statistics on cybersecurity data to develop machine learning integrated tools. These tools help in carrying out the necessary actions for threat detection and prevention.
Procedural Steps for Hunting
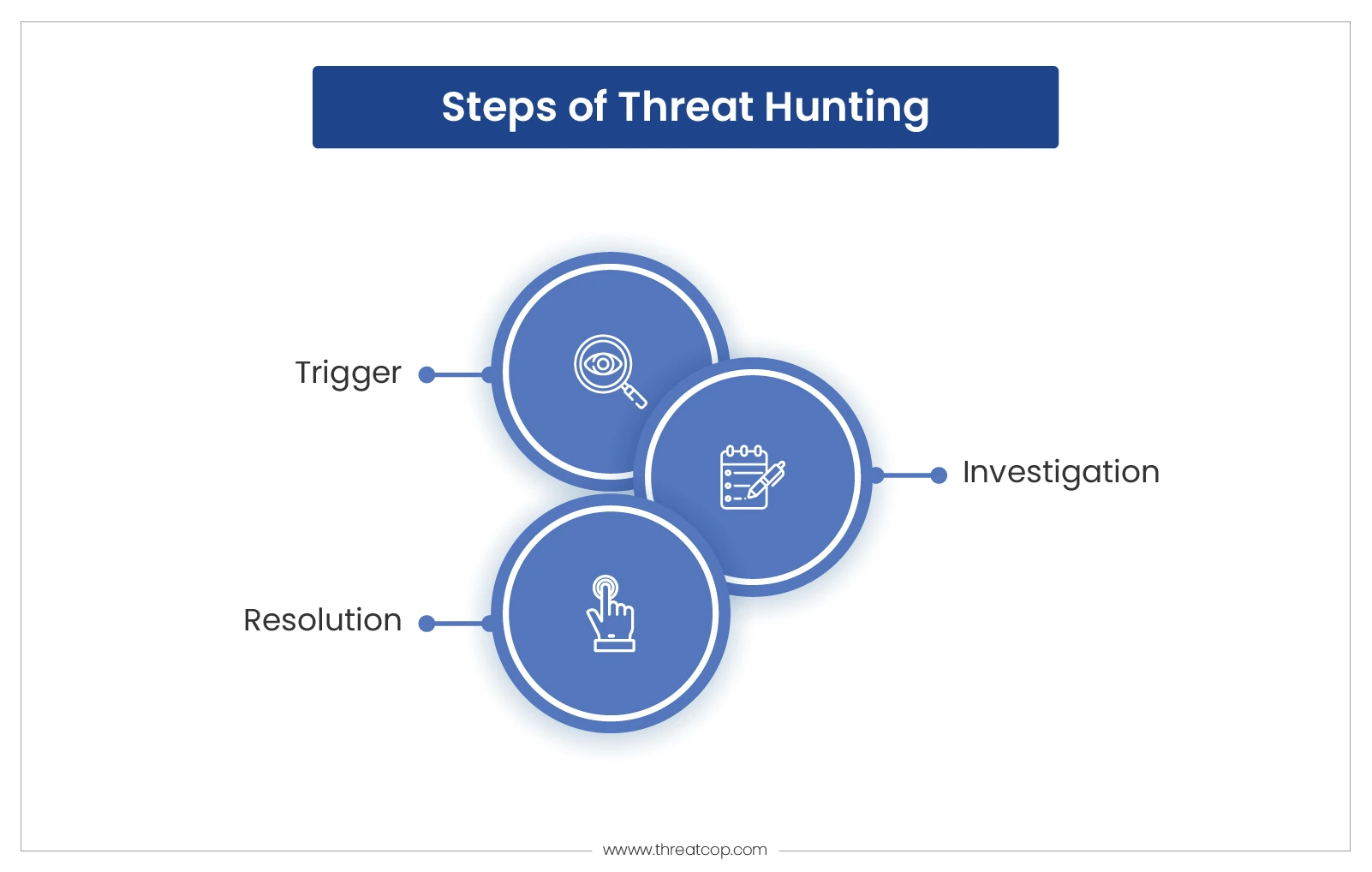
The technical aspect of carrying out threat hunting involves a set of procedures based on a proactive approach. Thus, a 3-step mechanism has been developed to identify and eliminate a threat.
- Trigger: A trigger can be any element, point of contact, or vulnerability that can lead to a cyber attack. In the process of threat hunting, the role of indicators, analytics-based hypotheses, and intelligence is prominent to learn about triggers. Thus, a trigger is the exact point in the cyber attack where malicious activity begins.
- Investigation: In this step, the technology of Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is used through multiple tools. They analyze the threat vector and trigger to record it and proceed with further resolution and prevention measures. This step presents a complete picture of the identified threat with its possible impact on the respective digital infrastructure of the organization.
- Resolution: The objective of this step is to respond and communicate to mitigate threats. This step involves a two-layered approach to mitigate threats. One is either taking predefined steps which are recorded in its system by a threat hunter or informing the respective cybersecurity team about the threat. For all the machine-based attacks, predefined action is taken, but human-based cyber attacks are usually mitigated through cybersecurity awareness training. This requires additional steps to be taken by respective organizations based on their vulnerability assessment to carry out customized employee cybersecurity training.
The Importance of Threat Detection and Prevention
According to IBM, every organization should have enterprise security for its cyber infrastructure. These security tools and services must collect all the data for every activity. The collective information is crucial for future threat prevention. Thus, threat hunting is itself a procedure of enhancing threat intelligence, which will be used to develop automated systems.
Threat hunting is important not only as a defense mechanism but also to provide information for future development. Threat hunting is itself based on huge amounts of data, and that’s why it is quite effective at securing the cybersecurity infrastructure. It acts as both a defense wall and an automated system that guards the wall.
Comparison with Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence is another term that is used in cybersecurity. The significance of threat intelligence is that it’s a database of information about successful intrusions or cyber attacks. The collection of data in this database is done mainly through automated security systems. In addition to this, vulnerability assessment and penetration testing data are also fed into the database. All of this data is comprehensively analyzed using machine learning and artificial intelligence.
Threat intelligence is extensively used in threat hunting. It means that threat intelligence is a fundamental necessity to carry out threat hunting. Threat intelligence is used as an essential database that provides parameters for threat hunting tools to prevent cyber attacks.
Hunting Models
Threat hunting involves an ocean of processes, approaches and techniques with the goal of detecting and preventing cyber intrusions. A threat hunting model is specified using a defined approach with inputs from processes, logs, and packets.
Then, it is fed with information about a particular attack vector. This helps in devising a specific threat hunting model. In common words, one can say that a threat hunting model is basically based on the application of threat detection and prevention. The following are some standard categories of threat hunting models.
Intel-based Threat Hunting
This model of hunting incorporates intelligence from IOCs. This model is reactive in approach, and its rules are defined by threat intelligence consisting of analytics and hypotheses. The investigation step provides the most crucial information that is used while developing this model.
Apart from IOCs, this model also takes in domain names, IP addresses, hash values, or other details gathered from the host. They are collected in the form of intelligence and retrieved from a platform in a specific way to be used in this model.
Hypothesis-Based Threat Hunting
The hypothesis is mainly a predictive kind of threat hunting model. Its approach is proactive, and a threat library is used to develop the model. This model incorporates IOAs and TTPs (attackers’ behavior) from threat intelligence for formulating hypotheses. Thus, a set of procedures is curated based on a particular hypothesis that is delivered using this model.
Customized Threat Identification
We’ve already talked about the methodologies, types, and steps of threat hunting separately based on their significance and application. The custom threat hunting model is a framework that takes a certain attribute from each of those segments based on the requirement. Threat hunters mostly use threat intelligence databases to develop some standard custom model that is specific to a particular industry or organization. Along with that, the cybersecurity team in the company is always ready to develop a customized model when a certain attack is launched and all the security mechanisms have failed.

Be Proactive and Safeguard Your Organisation
Every organization spends a significant amount of money to implement a cybersecurity framework in their organization. It becomes shocking and distressing to witness any cyber attack taking place. Thus, every organization needs a comprehensive program consisting of tools and services that can conduct threat hunting in their organization and strengthen cybersecurity.
Every organization must employ proactive tools and services that play the role of threat detection and prevention. An organization can install tools like TPIR to report suspicious emails and TDMARC to enhance email security. Apart from this, every enterprise should employ tools like TSAT to identify loopholes and vulnerabilities on a human level. The report generated from it can act as threat intelligence.
