As the world becomes more digital, so does the way we communicate and protect our information. Most attacks occur via email and are referred to as phishing attacks. In these attacks, attackers send their victims emails that contain information about the transfer of financial data or other sensitive information. However, these emails are easy to detect, and the security department can easily track them down. The success of phishing attacks depends on how realistic they are, and this requires skills. Many cybercriminals lack these skills, but phishing as a service changes that.
Table of Contents
ToggleAccording to a report, phishing attacks have increased by 61%. More than 3 million phishing attack reports have been collected from May 1, 2021, to April 30, 2022.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter On Linkedin
Sign up to Stay Tuned with the Latest Cyber Security News and Updates
What is Phishing as a Service?
Phishing as a Service (PaaS) is a kind of updated form of phishing attack execution. The attackers who carried out these attacks now charge for their services. Instead of carrying out the phishing campaigns themselves, the attackers help others to do so.
We all know that phishing attacks were carried out by attackers with a call-to-action text through which they deceived people. However, due to a lack of knowledge about the skills required for phishing attacks, this was not possible. Nowadays, attackers who are experts in performing phishing attacks offer a service-based course or software that helps the attackers in performing phishing attacks.
Phishing as a service is based on the SaaS (software as a service) business model, where customers pay a monthly fee to access a piece of software. This opens up a new source of revenue for cybercriminals and enables anyone to carry out more professional attacks.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
How Does Phishing as a Service Work?
The attackers have designed phishing as a service in such a way that even someone who is not an expert in it can still perform the attack.
Kit or Software
The Phishing as a Service kit was developed by attackers who carried out phishing attacks with the aim of generating more revenue. These kits are usually sold on the dark web, but some are now available on the surface web. The attackers simply designed a kit that can be easily purchased.
Pre-Defined Templates
Phishing as a Service offers many ready-made templates that can be used by attackers. The templates are designed to look like a real company’s email. The attackers who need to perform the phishing attack simply integrate the pre-made template according to the victims. For this reason, they can perform many potential phishing attacks that cyber criminals were not able to do.
Deploy Phishing Attack
Once the attackers acquire the Phishing as a Service kit, they are provided with a variety of templates, call-to-actions, images, ads, etc. that are very easy to integrate and send. Even if the attackers face problems, they have customer support available to solve their issues.
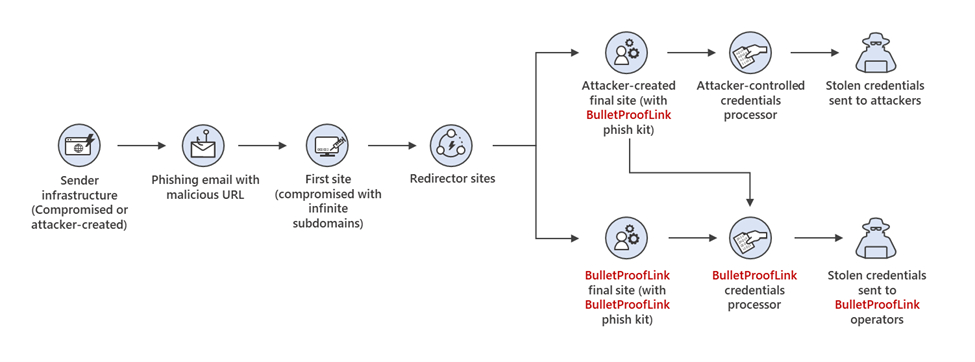
How can Organizations Tackle Phishing as a Service?
As technology evolves, hackers are also becoming more sophisticated. Thus, phishing as a service is also becoming more powerful. Companies must therefore implement cybersecurity practices to protect themselves from these phishing attacks.
Check For Sender
The first thing you should do is check the sender of the email. Many people have reported receiving phishing emails where the sender’s ID has changed. It is recommended to check the emails for fake sender names before entering the credentials.
Looks For Grammatical Errors
Most phishing attackers do not know much about grammar. Then check whether the email you received is professionally written or not. If there are any mistakes or doubts, you should not reply or click on anything mentioned in the email.
Don’t Open or Click Any Attachment
Phishing emails contain malicious attachments or links that can infect devices and steal sensitive data. Therefore, it is advisable to make sure that attachments do not contain any infections before opening them. To be sure that the received email is not infected, an organization should use a phishing incident response tool.
Employee Awareness
Employees are both the most valuable asset and the greatest threat because they are the primary target of any hacker. If an organization’s employees are not aware of the potential cyber attacks, it is easy for hackers to manipulate them. An organization should provide its employees awareness security training, so, that they are better protected in the future. It is important to provide employees with phishing awareness and simulation.
Conclusion: Phishing as a Service
Attackers use phishing as a service to deceive users in different ways. Both individuals and businesses are at serious risk from phishing attacks. However, hackers have improved their skills and now make kits to earn more money, they call it Phishing as a Service (PaaS). PaaS poses an additional threat because anyone can carry out such attacks without having the appropriate knowledge.
The introduction of PaaS has increased cybercrime and made each attack more effective. Far more credentials can be stolen with a phishing kit than with phishing emails, even if they are obvious. Companies should train their employees accordingly. Threatcop’s TSAT helps your company educate your employees about cyberattacks.
FAQs: Phishing as a Service
The main motive of hackers is to steal passwords, account numbers, bank details, etc., which can cause a lot of loss.
To recognize a phishing email, you need to pay attention to grammatical errors, email addresses, and much more. Because hackers are not well educated, and that is their only disadvantage.
Many phishing emails can be blocked by the DMARC protocol before they reach your inbox. However, scammers are outwitted, so adding more layers of security can be helpful.
The PaaS (Phishing as a Service) is a Software as a Service, which is being sold by the attackers as a kit on the dark web for the non-technical attackers to perform phishing attacks.
So, the phishing website is used by the attackers to fool users with authentic domain names and emails.
