Over the last few years, the education sector has become a new favorite target among cybercriminals. Numerous academic institutions have suffered from various kinds of cyber attacks in recent times, from turbulent ransomware attacks to covert data breaches. It has raised concerns leading to the incorporation of cybersecurity in the education sector as a necessity.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe introduction and adoption of newer technologies, along with the disruption caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, have fueled the situation further. Cybercriminals are attacking educational institutions with tactics and tools that have worked effectively against businesses.
Major Cyber Threats to the Education Sector
A wide range of cyber threats has been plaguing the education sector for years. Below are listed some of the major threats, each with an exemplary attack, hounding educational institutions around the globe.
- Spear Phishing Attacks: This attack vector requires extensive research by cybercriminals. An article on TechRepublic mentioned that from June to September 2020, around 3.5 million spear phishing attacks were carried out on educational institutions.
- BEC Attacks: Many times, threat actors have used business email compromise methods to target organizations in the education sector. In an article published by Dark Reading, 28% of all spear-phishing attacks on educational institutions were carried out for business email compromise scams.
- Ransomware: According to an article published by The Statesman, in a survey, it was found that almost half of the educational institutions globally were targeted by ransomware attacks in 2020. Among these attacks, 58% of the institutions found their data encrypted by cybercriminals.

- DDoS Attacks: Recently, on February 24, 2022, amidst the Ukraine-Russia war, a group of cyber attackers targeted educational institutions in Ukraine. It was found that around 100,000 attacks were carried out on 30 websites that are hosted by WordPress within 24 hours. On February 25, the number of attacks increased to 144,000.
- Data Breaches: This attack vector is meant to steal data from the organization and leverage it for financial gain or to exploit the organization. Recently, in March 2022, the University of Michigan suffered a data breach in which threat actors got access to the medical records of 2900 patients. This attack was levied after an email account of an employee got compromised.
- Email Hijacking: It is another form of a man-in-the-middle attack in which the hacker compromises and gains access to the email account of the victim. The attacker then secretly tracks the communication between the email sender and the recipient and uses the information for malicious purposes.
According to Threatpost, Purdue University detected 2068 phishing emails in 2020, followed by the University of Oxford (714), Stanford University (287), Hunter College (709), and the University of Buffalo (207).
Email hijacking is typically performed via phishing and other social engineering scams. In email hijacking, cybercriminals mislead victims to disclose their credentials by guiding them to fake login pages or tricking them to install malware.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
Why are Threat Actors Targeting Educational Institutions?
“It is more economically feasible to spend $1 million than potentially $10 million to retrieve the data.”
– Adam Hardi
(Higher education senior analyst at Moody’s Investors Service)
Data Theft
Universities and educational institutions have huge amounts of data. This data contains details of students, staff, vendors, and suppliers, and sometimes sensitive information like medical details. Threat actors use different vectors to land cyber attacks and steal this data, which they use to extort money from the institution or students individually.
The most damaging aspect of data theft is when threat actors get access to admissions-related data. This provides them with information such as social security numbers and academic information of students (further leveraging and selling it to placement or recruitment services).
Financial Benefit
Financial gain is the biggest motivation for cybercriminals. Ransomware attacks are one of the most damaging attack vectors because they inject malware into the target cyber infrastructure and freeze the operation, holding the data and leveraging it for ransom.
According to research, educational records are worth $265 per record on the black market.
Threat actors often look for other mechanisms to leverage the stolen data or information to make money out of it. In 2020, Forbes reported that the School of Medicine at the University of California paid $1.14 million as a ransom in response to Netwalker ransomware.
Espionage
Many popular and well-accomplished educational institutions and universities have research facilities. These facilities are a repository of various intellectual properties in the form of research data, especially associated with critical fields like medicine or engineering.
Threat actors can steal this crucial information and sell it to competitors. Sometimes they sell such intellectual property to other countries as well, which could influence economic policies. Additionally, they can hold data and demand a ransom for it.
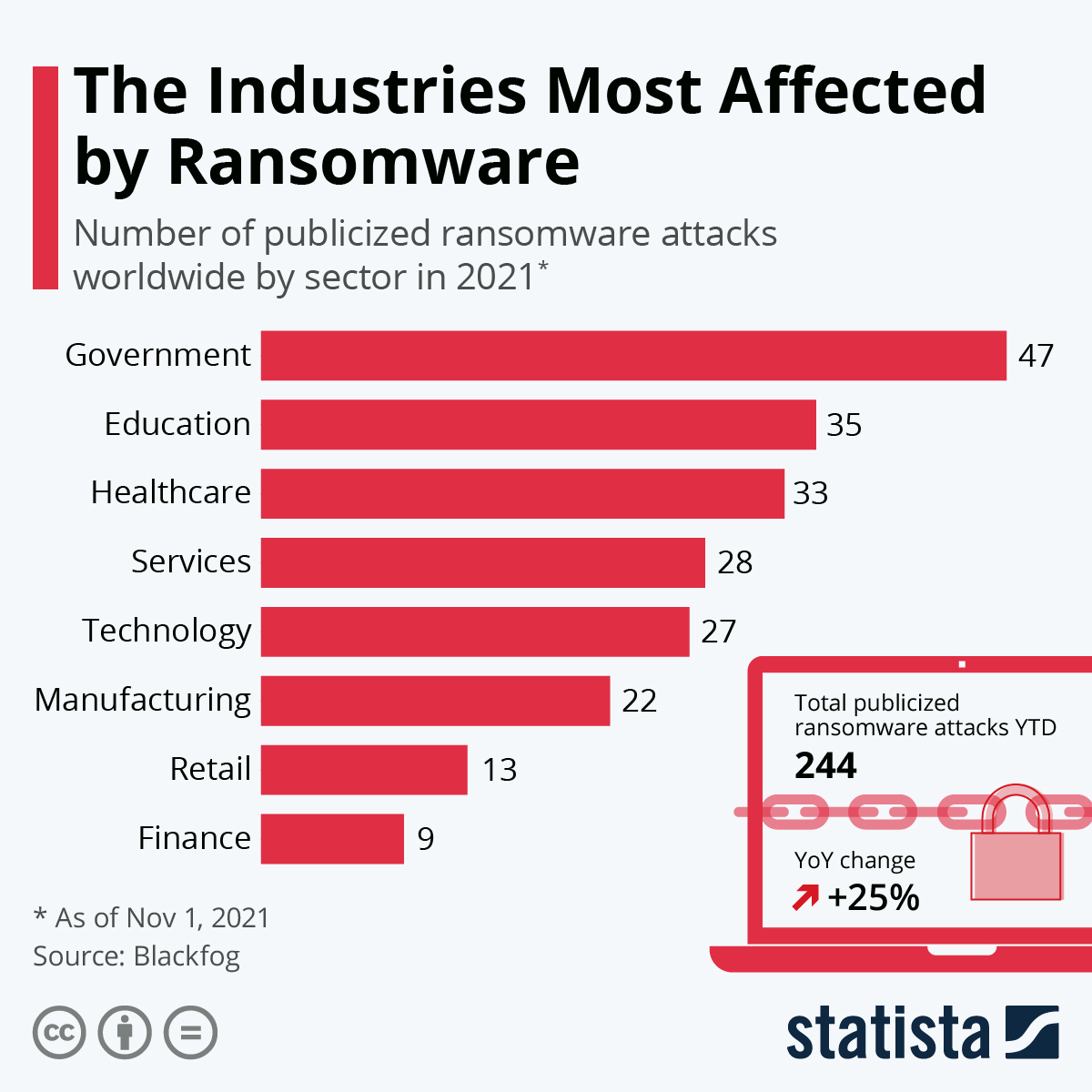
Cybersecurity in Education Sector and Institutions
According to a survey conducted by Moody’s, 30% of the higher educational institutions in the U.S. were using cloud technology in 2021, in comparison to 2% in 2020.
Cybersecurity is wholesome education and awareness training that is required for every kind of organization. One can understand from the above stats that educational institutions receive a large number of cyber attack attempts. That’s why these institutions need to adopt a set of cybersecurity learning and training for their employees.
How to Prevent Cyber Attacks in Educational Institutions?
Every educational institution needs to follow some guidelines and practices that will help them reduce the risk of attacks on the email domain. Additionally, these practices are meant to secure the organization from data theft and financial loss. Some of those guidelines are listed below:
Check the URL Carefully: A spoofed URL will have extra characters or fewer characters than the legitimate URL. Cybersecurity awareness will help individuals differentiate a spoofed URL from the original one and prevent phishing.
Be Vigilant About Suspicious Sources: Always check the sender’s address in the email. You should know whether you were expecting to receive the email or not. Scammers often send unexpected requests and warnings to create urgency.
Practice Website Bookmarking: It is advisable to bookmark legitimate websites so that you do not need to follow a link or type the URL each time you visit them. This also ensures the correct website loads each time.
Protect Outbound Emails: An email signing certificate is sometimes referred to as a S/MIME certificate or a personal authentication certificate. This certificate helps email recipients verify whether you are the actual sender of an email to them. There are two benefits of using this certificate:
- It defends your identity through the use of unique digital signatures.
- It provides secure and end-to-end encryption for your emails.
Email Authentication Protocols: Implement DMARC, SPF, and DKIM to combat domain forgery. These are a combination of authentication, reporting, and policy protocols that block unauthorized use of your email domain.
Cybersecurity Needs to be Part of Educational Curriculum
Cybersecurity awareness on an organizational level has become a dire necessity for the global corporate world. Many organizations are focusing on it as a part of regulation and training. But along with incorporating cybersecurity training in organizations, cybersecurity education should become a part of educational institutions.
Cybersecurity education should be a prominent part of the academic curriculum in universities and colleges. Apart from that, all the employees in educational institutions must receive cybersecurity awareness training to ensure that employees are vigilant and cautious enough to identify cyber attacks and prevent them from happening.
