Cybersecurity has become a national concern for most countries around the world. Like many other nations, India has been witnessing major changes and evolutions in its cybersecurity landscape. Owing to its substantial position in global geopolitics and high level of international recognition, the country has been increasingly becoming a popular target among cybercriminals. So, this blog will explore the current state of cybersecurity in India and how it is expected to change in the foreseeable future.
Table of Contents
ToggleAccording to the CERT-In, around 2,12,000 cybersecurity incidents occurred in the first two months of 2022 alone.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter On Linkedin
Sign up to Stay Tuned with the Latest Cyber Security News and Updates
As the Indian government has been pushing to digitize the country, the enterprises have rushed to digitize their processes and business operations. While this technological advancement has helped organizations to scale their business, it has also increased the risk of exposure to critical data and intellectual property theft. Ranging from cyber attacks on critical infrastructure to the new forms of the misuse of social media, India has been plagued by various cyber threats for years now.
Due to the precarious state of cyber security in India, the country has been at the receiving end of hundreds of meticulously planned and executed cyber attacks. Modern hackers have learned to utilize thousands of different techniques and methods for accessing information and money from organizations. Any organization that possesses sensitive data or relies on real-time computation has become a potential target of a cyber attack.
The cybersecurity market size in India is estimated to grow from ₹140 billion in 2019 to ₹290 billion by 2025!
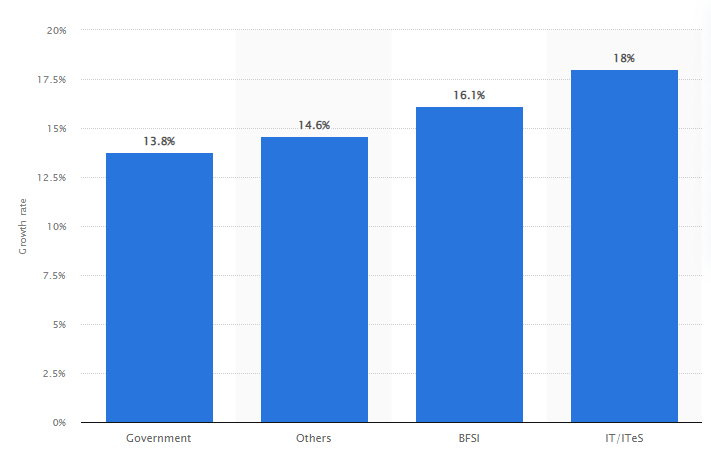
The State of Cybersecurity in India: By the Numbers
With the rapid increase in online frauds, data breaches, and cyber scams, India has become one of the most affected countries by cybercrime. Some statistics reflecting the state of cybersecurity in India are given below.
- Times of India reported that the number of ransomware attacks has increased by 120% in 2021 and 79% of all the Indian companies with an online presence have experienced at least one ransomware attack.
- According to an article by Livemint, around 1.16 million cyber attacks were reported in India in 2022, which was 3 times more than in 2019 and 20 times more than in 2016.
- An article by Inc42 revealed that ever since the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic, India has witnessed a 4000% increase in phishing emails and a 400% spike in the number of policy violations.
- In the same article by Inc42, 66% of organizations in India have suffered at least one data breach or cyber attack since shifting to a remote working model during the pandemic.
- According to a report by the FBI, India is ranked third in the world among the top 20 countries being victimized by cybercrimes.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
Notable Cybersecurity Incidents in India
Besides these spikes in cyber attacks and crimes, there have been a plethora of disastrous cyber attacks on organizations all over India.
- In May 2020, ed-tech startup Unacademy suffered a data breach that resulted in the compromise of the accounts of 22 million Indian users. The email addresses, usernames, and passwords of the compromised accounts were put up for sale on the dark web.
- In October 2020, the user data from the giant online grocery platform called BigBasket went up for sale in an online cybercrime market. The personal information of around 20 million Indian users was being sold for $40,000. The information on sale included names, email IDs, PINs, mobile numbers, password hashes, addresses, locations, dates of birth, and IP addresses.
- In January 2021, the COVID-19 lab test results of thousands of Indian patients were leaked online, seemingly by government websites. The leaked data was made publicly accessible on Google. The sensitive information included patients’ dates of birth, full names, the centers in which the tests were held, and testing dates.
- In February 2021, the personally identifiable information (PII) of 500,000 Indian police personnel went up for sale on a database sharing forum. The data was traced back to a police exam conducted on December 22, 2019. The leaked information included full names, email IDs, mobile numbers, dates of birth, criminal history, and FIR records of the exam candidates.
- India’s second-largest stockbroker, Upstox, suffered a data breach in April 2021 that affected its 2.5 million customers. Over 56 million KYC data files were leaked, including email IDs, date of birth, passports, PANs, etc. The infamous hacker group ShinyHunters gained access to the KYC details and contact data by compromising a third-party warehouse.
- In November 2020, the data of 1.4 million Indian job seekers were leaked online after a cyber attack on the job portal IIMjobs. The compromised data included the victims’ names, email addresses, phone numbers, the exact location of users, links to their LinkedIn profiles, and the industry of work.
Cybersecurity in India: What Lies Ahead?
Evolution of Cybersecurity
The organizations in the country and the overall digital domain are witnessing enormous progress. However, many things still need to be done. The government is set to implement cybersecurity and data protection laws to improve cyber governance in the country. The country needs more regulations to administer compliance and security standards for all organizations, especially government institutions. The government is also investing heavily in the development of infrastructure and conducting awareness campaigns.
Endpoint Security
Due to the pandemic, the world has quite largely adopted a remote work culture. The importance of endpoint security has risen significantly during that time. The usage of devices has increased and they need to be secured. The cybersecurity framework should include an extended detection and response (XDR) feature to accompany and strengthen traditional cybersecurity solutions.
Zero Trust Security Models
The zero trust security model defines the security framework of an institution or organization that involves every user, whether they belong to that organization or not, having to authenticate, authorize, and validate before getting access. The level of accessibility can also be defined in accordance with the type of user. This model is now being largely adopted by all organizations across the country. And most importantly, now the government has increased its involvement in implementing a zero-trust security model as a regulatory standard.

Required Approach for Cybersecurity in India
India is a developing country with several budding unicorn enterprises that are set to grow rapidly. At the same time, these organizations are the prime target for cybercriminals around the globe. That’s why organizations and the country as a whole need to invest heavily in developing cybersecurity infrastructure and installing a framework based on regulatory and standard compliance.
Organizations need to focus on empowering their workforce by carrying out cybersecurity awareness training for employees. It has become essential for organizations in India to enforce strict security protocols and follow the best cyber security practices. Only with the coordinated efforts of the public and the private sectors can the state of cybersecurity in India be stabilized and improved.
