Ransomware attacks are the most damaging and devastating cyber attacks for organizations around the world. These attacks not only expose confidential data but also incur massive financial damage to the victim organizations. As ransomware attacks continue to haunt businesses around the world, many new ransomware gangs are rising to fame. The Hive ransomware group is one of them.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe malicious activities of Hive ransomware started coming to light in 2021. They adopted the RaaS model to carry out a series of infamous attacks through affiliates. The group seeks new affiliates by proposing values of transparency and operational efficiency. The group pursues sustainability by developing an environment that could incorporate stronger and bigger affiliates. So, let us dive deeper into the workings and functioning of this ransomware group.
Who is the Hive Ransomware Group?
The Hive ransomware group is a new addition to the list of several infamous ransomware groups that pose a great threat to businesses worldwide. The group operates through the ransomware as a service (RaaS) model and targets some specific sectors, such as healthcare institutions, energy companies, etc. Since its inception in June 2021, it has been found to be one of the most active ransomware groups.
The threat actors in the group operate through a fake website with .onion as an extension. The website is used for naming and shaming ransomware victims. Hive ransomware group initially targets organizations or users through phishing emails. After getting access to the victim’s network, they execute a remote desktop protocol (RDP) to navigate through the victim’s servers and network.
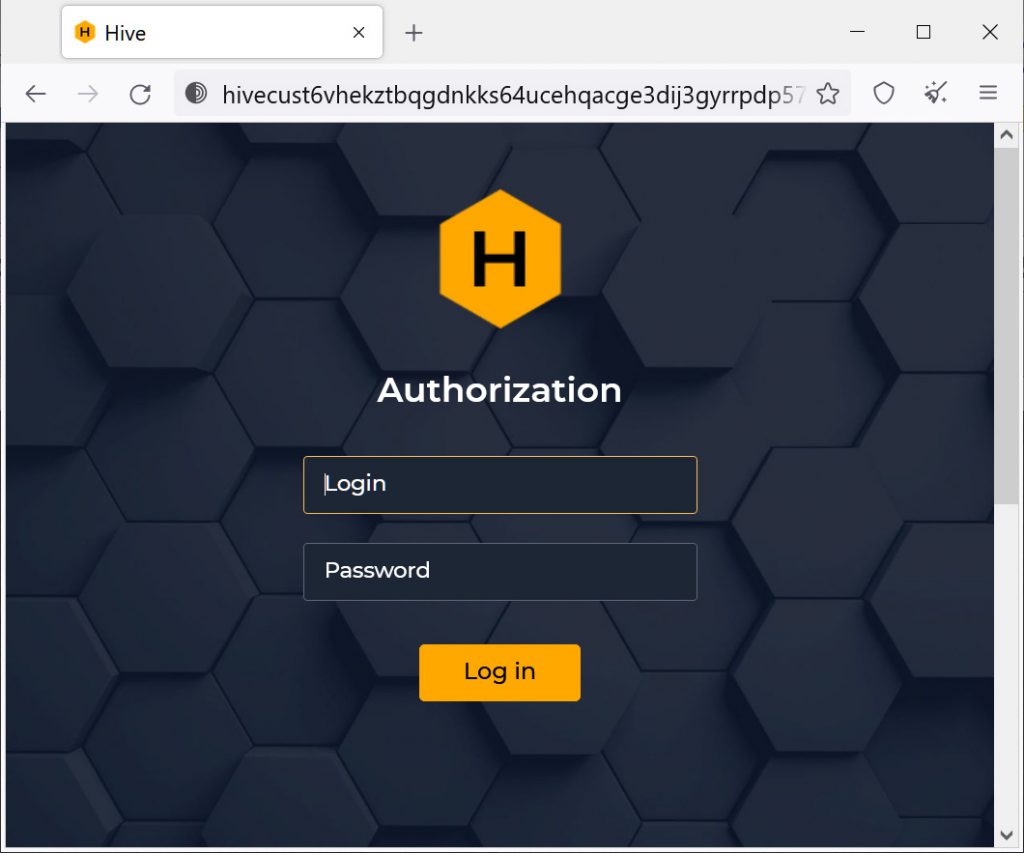
How Does Hive Ransomware Group Work?
The Hive ransomware group employs the ransomware as a service (RaaS) method to carry out their attacks. The group employs affiliates and carries out malware-based attacks primarily on non-profit retailers, healthcare organizations, energy providers, etc.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
The group employs ransomware tactics, techniques, and procedures to target users’ devices. The affiliate operator disables anti-malware protection and then infiltrates the victim’s data and business files. The affiliates primarily rely on phishing emails containing malicious attachments or leaked credentials of VPNs. The affiliate places a ransom note in plain text to threaten the victim with leaking their data on the Tor website unless they meet the conditions of the affiliates.
The affiliates employ a mechanism of double extortion that involves compromising corporate data from the target organization and then decrypting the disk. If the victim user refuses to pay the ransom for the decryption key, the threat actors threaten to reveal the name of the organization and the stolen data all over the leak site and set a timer for publicizing. This provides hackers with an opportunity for extortion.
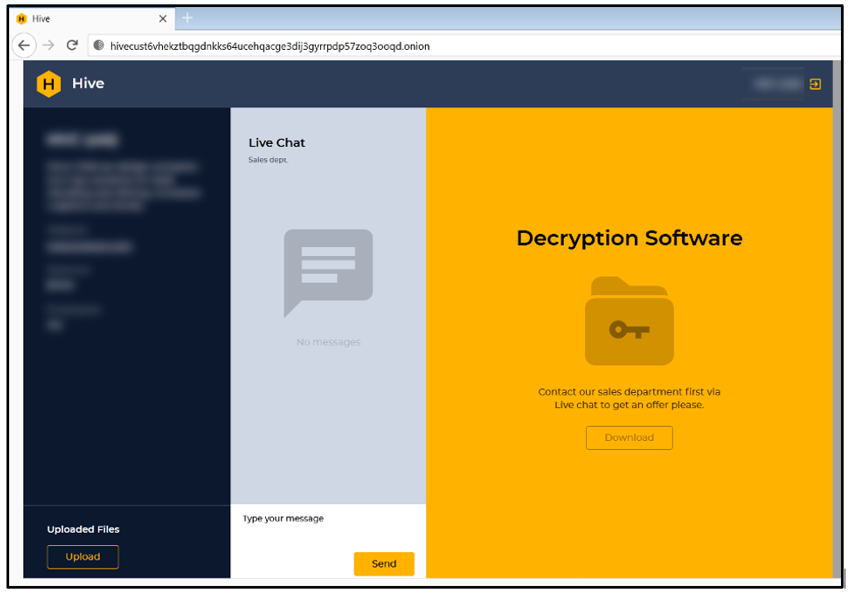
Infamous Attacks by Hive Ransomware Group
Hive ransomware group has been responsible for a number of massive cyber attacks on well-known companies worldwide. Some of these attacks are mentioned below.
Microsoft Exchange Servers are the Favorite Target
The Hive ransomware group’s favorite target is the Microsoft Exchange server, which they have been consistently targeting. The attack took place on April 19, 2022, and was identified and investigated by a cybersecurity firm’s forensics team. Several services and devices were affected by the attack.
The ransomware group attacked ProxyShell Exchange Security vulnerabilities, which have also been previously targeted by other ransomware gangs such as Conti. The ProxyShell is the upgraded version of an earlier attack that was known as the ProxyLogon. The three vulnerabilities identified in ProxyShell attacks are marked as CVE-2021-34523, CVE-2021-31207, and CVE-2021-34474.
While these vulnerabilities had already been patched by Microsoft last year, many users and companies still haven’t carried out their Exchange server update installations. After getting access to the target organization’s systems, the affiliates placed a malicious script as a backdoor, which was publicly accessible. This script could execute PowerShell code on the compromised server.
Then the affiliates downloaded the command and control server, which is associated with the Cobalt Strike framework, leading to the installation of other tools. Then affiliates scanned the server and found confidential information before deploying ransomware.
Missouri Hospital Under Attack
The hive ransomware group is infamous for targeting the healthcare sector, showing no regard for humanitarian considerations. The Missouri Delta Medical Center was targeted by the group in early September 2021. The medical facility issued a statement confirming the breach, citing that unauthorized access had stolen confidential and sensitive information from their servers. The group then started posting the details of the patients online, including their names, medical conditions, and social security numbers. Later, the FBI issued a flash alert for other organizations about Hive ransomware. They also provided the required guidelines to detect, prevent, and respond to any malware attacks.

A Non-Profit Memorial Health System Suffered a Breach
A month before the attack on Missouri Hospital, the Hive ransomware group had claimed to have carried out a ransomware attack on Memorial Health System that led to EHR downtime, diversions in the emergency room, and appointment cancellations. The Memorial Health System is a network of three hospitals, several provider clinics, and outpatient service sites. The attack was discovered when several computers in the facility were found to be encrypted, which forced the staff to work with paper charts.
This attack led to the disruption of various medical and financial operations, causing the cancellation of radiology exams and surgical cases. There was no confirmation about whether the data of employees had been compromised or not. But the patient’s data was likely to be compromised.

Wrapping Up
The Hive ransomware group is relatively new to the business, but they have quickly become infamous. The activities of the group are extremely frequent in numbers and it is widely regarded as one of the most aggressive ransomware groups. Their attack mechanism is quite strong, and they continuously seek new affiliates. The most dangerous aspect of this group is that they are continuously improving and diversifying their TTP, which has become challenging for various organizations.
Organizations around the world need to be more vigilant and careful about their cybersecurity framework. The initial attack vector of the Hive ransomware group is phishing emails. So, organizations can train their employees to detect and avoid phishing emails. Organizations must carry out comprehensive cybersecurity awareness training for their employees. They need to evaluate the employees’ vulnerability levels through phishing simulation techniques and generate their EVS (employee vulnerability score) to carry out targeted learning activities.
Organizations need to employ a robust security framework through awareness training and phishing incident response tools to educate and empower their employees to prevent every kind of email attack. The phishing incident response tool allows organizations to enable their employees to report and check suspicious emails and eliminate phishing emails.
So, buckle up and prepare yourself. The only way to protect yourself against the Hive ransomware group and other similar threats is to stay vigilant and plan ahead.
Senior Writer
Shantanu is an accomplished content strategist and technology enthusiast at Threatcop Inc. With a knack for translating technical intricacies into reader-friendly narratives, Shantanu contributes to making cybersecurity insights both informative and enjoyable for tech enthusiasts and general audiences alike.
Senior Writer Shantanu is an accomplished content strategist and technology enthusiast at Threatcop Inc. With a knack for translating technical intricacies into reader-friendly narratives, Shantanu contributes to making cybersecurity insights both informative and enjoyable for tech enthusiasts and general audiences alike.
