In the current era, where data holds immense value, a single data breach can potentially impact individuals, damage a brand’s reputation, and leads to financial losses ranging from hundreds of millions to billions. An example of such an incident occurred with OCBC Bank, which incurred a financial loss of $13.7 million due to an SMS phishing scam. It is shocking to observe that despite the risks, people’s naivety leads them to overlook the threat posed by SMS phishing, making them susceptible to falling victim to such attacks.
Table of Contents
ToggleSubscribe to Our Newsletter On Linkedin
Sign up to Stay Tuned with the Latest Cyber Security News and Updates
The above data breach shows social engineering-led attacks are more prevalent nowadays. According to a report over 700 social engineering attacks take place yearly in an organization. And one such attack happened with Coinbase where a social engineer cum hacker led an SMS phishing attack to gaincompromise the user’s data. In this blog, we will get you down to the details of the attack and discuss the importance of prioritizing cybersecurity in today’s business environment.
How Social Engineering Exposed the Confidential User Data of Coinbase?
The popular Coinbase cryptocurrency exchange platform has disclosed that the so-called “0ktapus” hackers stole the login credentials of one of its employees. Threat actors attempted this to remotely gain access to the company’s systems. The hackers were able to access some contact information belonging to multiple Coinbase employees as they viewed the dashboard of several internal communication tools. Along with this, they get their hands on user information from the corporate accounts of employees.
Allegedly Oktapus has targeted more than 130 tech and video game companies in 2022 which include Twilio, Cloudflare, MailChimp, and Signal. In the ongoing effort to get control of the login information of thousands of employees, they frequently pretended to be legitimate login sites. This is according to a leaked CrowdStrike report seen by TechCrunch.
Following the attack, Coinbase shared the findings of their investigation to alert other companies, identify the threat actor’s tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), and set up appropriate defenses. We came to know how the hackers executed this attack.
Here is the Detailed Breakdown of the Coinbase Data Breach
On Sunday, February 5, the attacker sent an SMS labeling it as an “Important corporate notification” to a number of Coinbase employees asking them to connect to their corporate accounts to receive a crucial message. The message spoofed “important corporate notification” SMS to five employees with a phishing link to a website impersonating the Coinbase corporate login page, which was actually a malicious landing page intended to steal credentials.
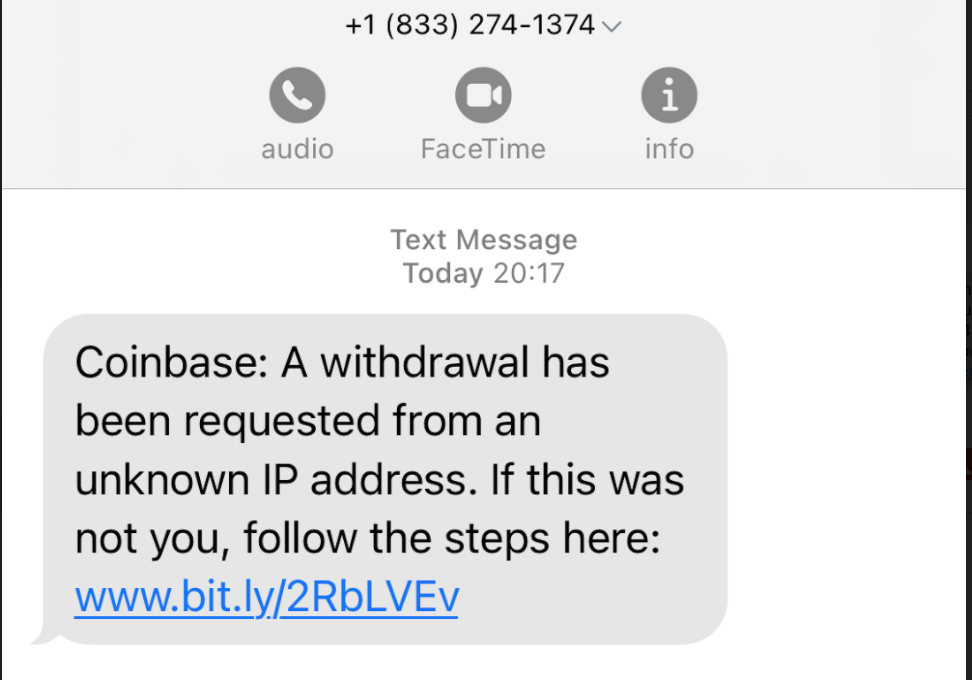
Many employees disregard that message but one fell for the ruse and clicked the link to the phishing page and entered his credentials. The page displayed a thank you message for verifying the information and securing the account and told them to ignore the message after inputting their credentials.
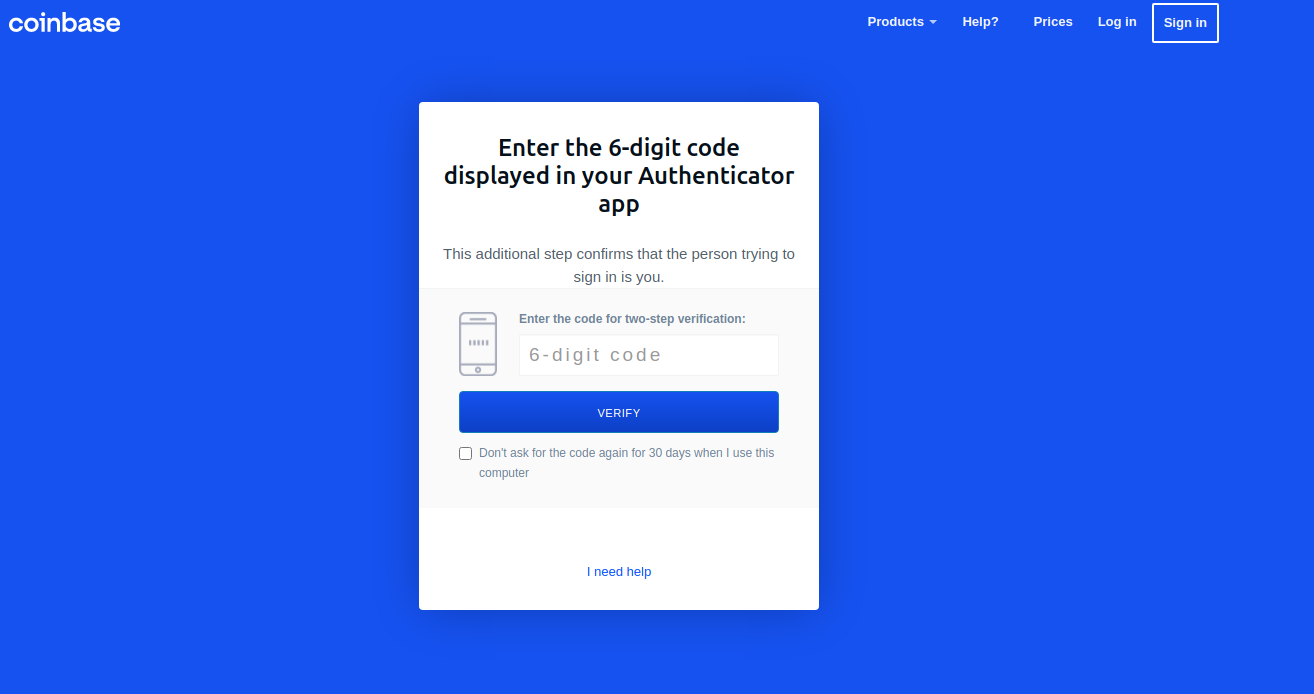
The attacker then attempted to use the stolen credentials to get into Coinbase’s internal systems but was unable to do so because access was restricted by multi-factor authentication (MFA). Coinbase has employed Yubikeys, a hardware token used to generate 6 – a digit codes for MFA.
After a few failed attempts, about 20 minutes later, the attacker switched to a different plan of attack known as vishing or voice phishing. The hacker then impersonated a security guy and called the employee who initially compromised credentials. The victim was instructed to enter their workstation and asked to install AnyDesk followed by ISL Online for the security guy to carry out some crucial steps
You can also check out more on Vishing Training and Simulation
This was set up with the intention of installing a program called EditThisCookie, which is used to retrieve passwords and access tokens from web browsers. As the hackers got access to the employee’s corporate account through AnyDesk, they installed EditThisCookie plugin to record all the passwords and hardware tokens. In the process, the hackers gained access to the employee’s corporate directory, which contained Coinbase’s customer data. This method of carrying out a security breach is known as lateral movement, where one compromise leads to another until the whole system is exposed.
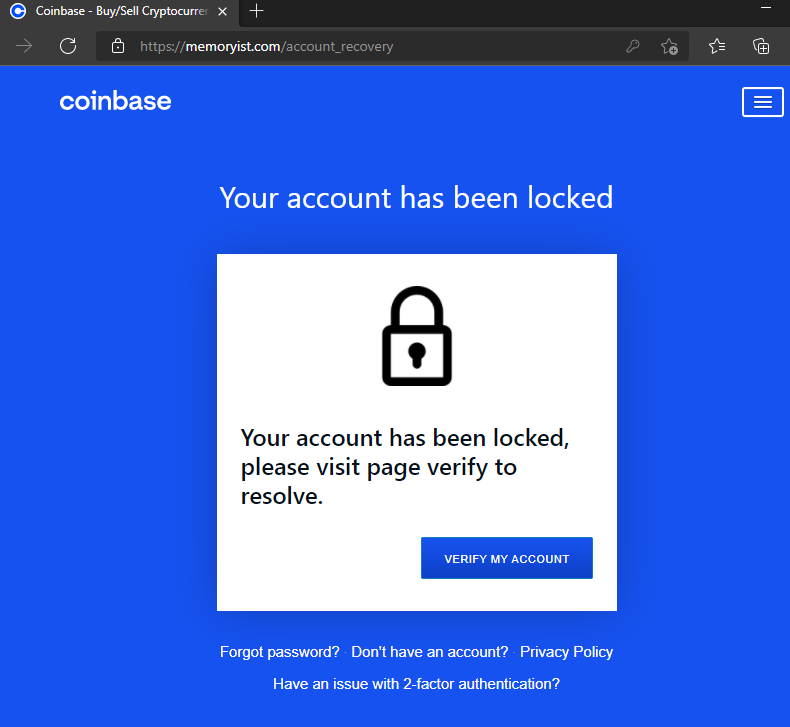
According to Coinbase, they got an alert within the first 10 minutes of the breach attack, and its security team reached out to the victim to inquire about the suspicious activity from their account, directing the employee to cut down all communications with the adversary. This happened because Coinbase employed the XDR (Extended Detection and Response) tool, which identified an unusual pattern of operation in the employees’ workstations and warned the security team of the company.
However, Coinbase released an official statement where they stated that their system suffered a security breach for a while, which exposed some of their customers’ data. They urged others to be on the lookout for potential attempts to install remote desktop software such as AnyDesk or ISL Online as well as a legitimate Google Chrome extension called EditThisCookie.
You can read more about– SMS Phishing Scam: OCBC Bank’s Customers lost $8.5 Million
What is Coinbase’s Take on the Data Breach?
While talking to TechCrunch, Coinbase spokesperson Jaclyn Sales said that a threat actor was able to view the dashboard of a small number of internal Coinbase communication tools and access limited employee contact information. Coinbase claimed that no customer data was accessed, but the company’s chief information security officer, Jeff Lunglhofer, recommends users consider switching to hardware security keys for stronger account access but did not say whether it uses hardware keys internally, which cannot be phished.
“The threat actor was able to see, through a screen share, certain views of internal dashboards and accessed limited employee contact information. Our security team was able to detect unusual activity quickly and prevent any other access to internal systems or data,” Sales added.
This attack was not new to Coinbase as the company was breached in 2021 as well. In the last quarter of 2021, hackers gained unauthorized access to data from the Coinbase cryptocurrency platform. The cryptocurrency corporation responded to the hack by notifying more than 6,000 clients of the breach and its potential repercussions. Although the attack ended with the theft of cryptocurrency, it also had the potential to result in identity theft.
What was the Nodal Point of the Coinbase Data Breach?
Similar to numerous other social engineering-driven attacks, the Coinbase data breach also arose from the negligence of its employees, ultimately resulting in a security breach. It is worth emphasizing that humans remain the most vulnerable targets within any organization. Had the Coinbase employees possessed sufficient awareness to identify the initial fraudulent SMS, the attack could have been thwarted from its inception. Furthermore, the vishing attack succeeded due to the employee’s failure to ascertain the legitimacy of the individual on the phone, who purported to be an IT professional affiliated with Coinbase.

Uber security breach (2022) is another instance of human error where an employee ended up giving credentials to a duped co-worker. Threat actors used it to get full access to the cloud-based systems where Uber holds critical consumer and financial data.
A recent report ‘Security in the Age of AI’ mentioned that C-Suite executives and policymakers rank ‘human error’ as the top cybersecurity risk for their organization. And research by IBM Security says that data breaches happened due to employee negligence are 95%. The top cybersecurity organization and Researchers from Stanford University revealed that approximately 88% of all data breaches are due to human errors. Human error is still the driving force behind an overwhelming majority of cybersecurity problems.
Read more about: The Threat of Smishing is on the Highland
How Could Employees Have Prevented the Coinbase Data Breach?
Although Coinbase’s security team identified the breach before significant damage occurred, the employees could have played a crucial role in preventing the attack. The employee who fell for the phishing link lacked proper cybersecurity training and awareness. Firstly, if the employees had been provided with tools or training to check the legitimacy of URLs in phishing messages, they could have identified the suspicious link and halted the attack.
Furthermore, if they had been educated about social engineering tactics and the importance of verifying the legitimacy of requests for sensitive information or actions, the employee who fell for the vishing attack would have been able to recognize that the individual on the phone was not genuine IT personnel.
According to Frontier magazine, 83% of organizations have seen voice phishing attempts to obtain OTPs or authorize MFA login. Employees need to be trained to recognize social engineering tactics and verify the identity of any person or medium, which requests or demands sensitive information or asks them to perform a certain action.
Did Coinbase Data Breach Cause Financial Damage?
Although Coinbase reported that no customer data was accessed during the data breach, it still incurred significant costs. According to a filing with the US Securities and Exchange Commission, Coinbase is estimated to lose $1.1 million in revenue due to the data breach. The company also faced legal and regulatory scrutiny, which could further impact its reputation and revenue.
Read more about: What is Spear Phishing Attack and How Can It be Prevented?
What Does Global Data Say About Data Breach?
In a report published by RiskBased Security, there were 1,767 publicly reported data breaches in the first six months of 2021, exposing 18.8 billion records. The report also found that the number of data breaches increased by 24% compared to the same period in 2020. This data highlights the global scale of cyberattacks and the need for businesses to prioritize cybersecurity.
The threat of cyberattacks on companies is a growing concern globally.

According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, the global cost of cybercrime is expected to reach $10.5 trillion by 2025. The report also highlights that there will be a new ransomware attack every 11 seconds by 2021. Here are some more statistics about cyberattacks faced by companies globally:
- In 2020, the number of cyberattacks on businesses increased by 20% compared to the previous year. It was reported by Accenture.
- IBM published a report that mentioned that in 2020, the average cost of a data breach was $3.86 million.
- 95% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error, said Cybint Solutions
- According to HIPAA Journal In 2020, the healthcare industry was the most targeted industry by cybercriminals, with 79% of healthcare organizations experiencing a data breach.
- The financial services industry is the second most targeted industry by cybercriminals, with an estimated cost of $18.3 million per organization, Accenture quoted.
- In 2020, there were 16 billion records exposed in data breaches. (source: RiskBased Security)
- Phishing attacks remain the most common type of cyberattack, accounting for 80% of all reported security incidents. (source: Verizon)
These statistics show that cyberattacks are a significant threat to companies globally and can have severe financial and reputational consequences.
Check out- Ransomware Statistics: What Data and Trends Say?
How Can CISOs/CIOs Prevent Their Business from Such Attacks?
Do you feel that your employees are equipped and trained enough to prevent data breaches at their level? Employee negligence or unawareness can lead to horrible loss to your company’s reputation and financial state and cybersecurity training is the need of the hour. The C-suites need to take robust steps to improve their company’s cybersecurity posture.
Here is how the C-suite can prevent their business from cyber-attacks based on social engineering:
Regular Training
Regular employee training is the primary defense against social engineering attacks, including phishing, pretexting, baiting, and quid pro quo. Education should cover identification and response methods for these common attack methods, as well as warning signs in various forms of communication.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
Implement Security Protocols and Policies
Establishing clear security protocols and policies is critical to prevent social engineering attacks. Policies should include guidelines on data access, sharing, and storage, and protocols for handling sensitive information. It should also outline the steps to be taken in case of a security breach or data theft.
Organizations must use smishing simulation and awareness training by TSAT to teach staff about smishing attack assaults, how they are led, and how they may be prevented in order to prevent attacks like the data leak in Coinbase. Humans are the easiest target of attacks happening through social engineering and once they are trained and equipped they can sense and prevent any such attacks.
Also Read: How is Information Security Shaping the Cyber World in the Middle East?
FAQs: Coinbase data Breach
According to Coinbase, the attack was most likely carried out by 0ktapus. They are highly skilled cybercriminals that also target Twillio, Cloudflare, and at least 130 other companies with identical spoofed SMS-based text messages.
It is crucial to act right away if your Coinbase account is hacked and you find that money has been taken out without your permission. To start an investigation into the situation, get in touch with your local law enforcement agency. Make sure the law enforcement officials speak with Coinbase directly as well, as the firm is committed to working closely with any legal inquiries regarding their platform.
In general, leaving money in your Coinbase account is considered safe. Yet, there is always a chance that your personal information could be hacked, thereby allowing unwanted access to your account, as with any online site. To avoid this risk, it is vital to keep your password safe or have basic knowledge of cyber threats.
Security awareness training can be an effective weapon in the fight against social engineering attacks which was faced by Coinbase. Organizations can assist prevent breaches brought on by human error or neglect by educating and training personnel on the best cybersecurity practices and data protection. This training can assist people in identifying and rejecting any spoofed SMS text messages. Hence, organizations should incorporate smishing awareness and simulation training programs. CISOs can take the help of Threatcop Security Awareness Training (TSAT), which includes a smishing simulation element and an innovative learning management system (TLMS).
Smishing is made of two words SMS+Phishing. It remains one of the most common and effective methods used by cybercriminals to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information. Smishing simulation and awareness training help people recognize and respond appropriately to these threats. Smishing awareness is important for organizations as employees can be vulnerable links.
Yes, there are reliable smishing simulation tools available, and one such tool is the “Smishing Awareness Training” offered by Threatcop. These tools are important for organizations as they allow them to simulate realistic smishing attacks, test the awareness and response of their employees, and identify vulnerabilities in their security systems. The Smishing Awareness Training tool by Threatcop specifically focuses on educating individuals about smishing threats, training them to recognize and respond appropriately, and reinforcing a culture of cybersecurity within the organization.
Security Compliance Executive
Department: Compliance, Threatcop
Sanjana is a Security Compliance Executive working on best-of-the-industry-level compliances relevant from a cybersecurity perspective, their implementation, learning and outcomes in various business domains.
Security Compliance Executive Department: Compliance, Threatcop Sanjana is a Security Compliance Executive working on best-of-the-industry-level compliances relevant from a cybersecurity perspective, their implementation, learning and outcomes in various business domains.

