Most people use the internet and search for different domain names to find the specific websites that they want to visit. But the computer won’t understand the domain names, as it only understands and uses the IP addresses to identify the website and browse it. The majority of people don’t worry about DNS security or give much thought to the domain name system.
Table of Contents
ToggleTo make website browsing easier for users, DNS was introduced. The DNS, or Domain Name System, is a protocol that is used to determine the IP address of the website once the users enter the domain names.
The DNS made the work for the users very simple, as they don’t need to type a long and unmemorizable IP address. Since it can connect users to websites or internet-enabled applications, effective DNS servers are characterized by their invisibility. However, there is a catch to this invisibility. Threat actors frequently stage cyber attacks using the DNS layer because the majority of organizations don’t bother to secure it. In this article, we will discuss DNS security.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter On Linkedin
Sign up to Stay Tuned with the Latest Cyber Security News and Updates
What is DNS Security?
Each organization implements its own DNS infrastructure for its websites and services. However, hackers try to hack it and perform some DNS security threats so that they can penetrate the system.
Organizations generally trust DNS, so their traffic is frequently permitted to pass through network firewalls. Cybercriminals frequently target it and take advantage of it, though. Therefore, DNS security is a crucial aspect of network security.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
The companies follow different DNS security strategies during the implementation of DNS, so, attackers can’t get into the system. During the DNS Security implementation, the companies follow some different overlapping defenses, add some redundant servers, apply different security protocols, DNS logging, etc. They implement all this, so that, they can build good protecting DNS security.
Why is DNS Security Important?
“More than 72% of organizations faced DNS attacks in 2021”
The DNS system is not designed with the feature of security within it. Due to this, it has several design limitations. These security limitations can be a way for hackers to get into your system.
Most companies implement their own DNS security so that they can prevent DNS security threats. They do this by performing different DNS security tests through which they can secure DNS. However, there are a lot of methods by which cyber criminals perform DNS attacks.
DNS Spoofing
DNS spoofing is one of the methods used by hackers to attack DNS servers. In this attack, the hackers inject the forged DNS data into the resolver’s cache. By which the DNS will start returning the wrong IP address which is thereafter used by the hackers. Those wrong IP addresses direct users to a specific malicious website or another desired website created by the hackers.
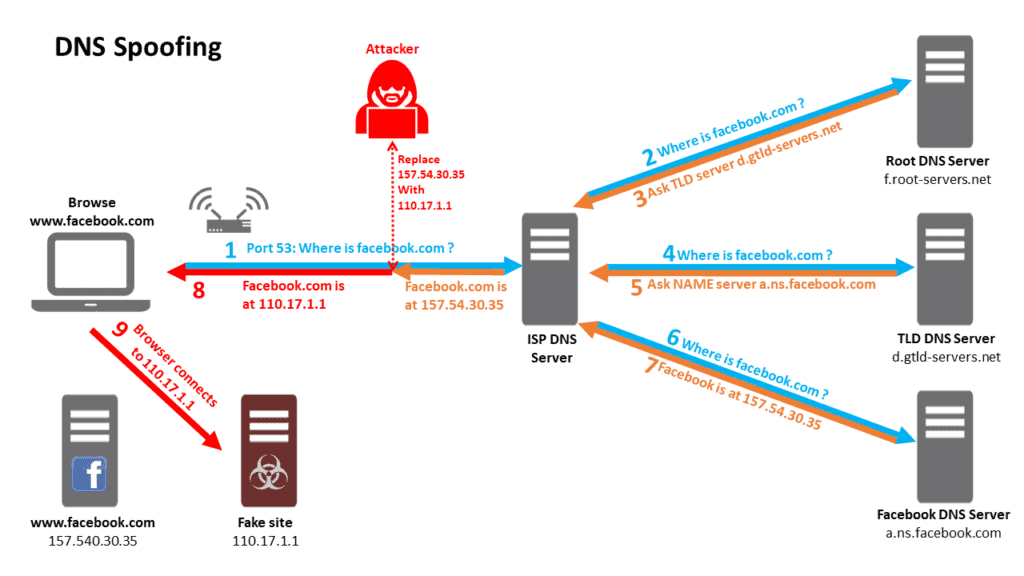
In 2018, the hackers compromised Amazon’s route server and the public Google DNS server, and by doing so, they re-routed around 1300 IP addresses that were pointing to some malicious websites.
Hijacking
Hijacking is another method of attack where attackers redirect all the queries to a different domain name that has been designed by them. This can easily be done with the help of malware or unauthorized changes to the DNS server. However, the result will be similar to DNS spoofing, as the hackers will again point the users to a different website that is organized by them.
Tunneling
DNS tunneling is another type of attack where the attacker uses other protocols through DNS queries and responses. The hackers can use TCP, SSH, or HTTP to pass malware to the DNS server or steal information that is in the DNS queries, which is not detected by the firewalls.
Phantom Domain Attack
Just with the name phantom domain which means ghost domain. Here, the attacker sets up a lot of phantom domain servers that will respond to the requests very slowly or not at all. Then the resolver gets flooded with a lot of requests after waiting for the response for a long time. It then leads to the slow performance of the website or block the services.
Random Subdomain Attack
The random subdomain attack is another way in which the hackers send DNS queries for several random or nonexistent subdomains of any legitimate site. In this method, the hackers want to create a denial-of-service for the domain’s authoritative nameserver. It is also possible that the ISP serving the attacker may be affected by this vulnerability. This is because the cache of their recursive resolver will be filled with erroneous requests as well.
Protective Steps for DNS Security
The hackers target only those organizations that are not properly securing the DNS. Several ways have been developed to secure DNS servers, such as:
Use DNS Forwarders
It is a DNS server that performs DNS queries on behalf of designated servers. The primary reason for using DNS forwarders is to offload processing duties. The other benefit of using a DNS forwarder is that it will prevent the DNS server from forwarding requests and interacting with Internet servers. It is very important when your DNS server is hosted with internal domain records.
Use Caching-Only DNS Servers
Caching-only DNS servers are not authoritative for the DNS domains. It is configured to perform recursion or use a forwarder. When it receives a response, it then caches the result and returns the answer to the system that issued the DNS query to it. It can improve the security of your organization when used as a forwarder that is under your administrative control. Using our own caching-only DNS servers as forwarders will increase DNS security, as you don’t have to depend on your ISP’s DNS server.
DNS Resolvers
The DNS resolver is a DNS server used for recursion to resolve names for domains for which this server is not authoritative. The benefit of using a resolver is that it will work on a dedicated DNS server, which works to resolve host names. Due to this, there will be more security for your own DNS server, and there will be DNS security threats.
Disable Zone Transfers
The zone transfers take place between the primary and secondary DNS servers. The primary server is authoritative for specific domains that contain writable DNS zone files, which are updated whenever needed.
The secondary servers received a read-only copy of these zone files from the primary DNS servers. A secondary server is used to improve DNS query performance throughout an organization.
The attackers can use this information to attack the infrastructure services. So, your organization can set it so that only zone transfer requests that are from the inside and from the specific servers should be accepted otherwise, they should not.
Keep Your DNS Servers Updated
A lot of organizations and users forget to keep updating their DNS servers, which makes it easier for the attacker to get into the system. So, the organization needs to keep its DNS servers updated to prevent attacks from hackers.
Restrict Zone Transfers
Restricting the zone transfer is important, to restrict the server’s zone transfer to protect it from cyber attacks. You can easily restrict your zone transfer file by adding some conditions to the DNS zone configuration. Once it is added, the attackers will not be able to transfer the zone.
Conclusion: DNS Security
Cybercriminals always try to target your DNS server to get into a network. Having a secure DNS and security system can prevent it from happening. Therefore, every company needs to be aware of the biggest security dangers that DNS poses.
Understanding what organizations can do to ensure DNS security is also essential. Most importantly, they should look for cybersecurity practices that rely on cutting-edge threat-hunting components and attempt to automate security tasks. With Threatcop, your organization can secure itself from cyber threats.
FAQs: DNS Security
Why is DNS security important?
DNS security is important because it prevents attackers from getting unauthorized access. In other words, the internet as we know it would not exist without it.
Does DNS turn domain names into IP addresses?
The DNS is the domain name of a specific website that points to the computer by converting it to IP addresses so that it can be understood by the computer. DNS servers convert IP addresses into friendly URLs or domain names. They convert user input into something a computer can understand in order to locate a webpage. DNS resolution refers to the translation and lookup processes.
Why is DNS security important?
In simple words, if there is no DNS, then there is no internet. The Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) also ensure the security and confidentiality of data and defend DNS against dangers like cache poisoning. DNSSEC servers digitally sign each server response.
