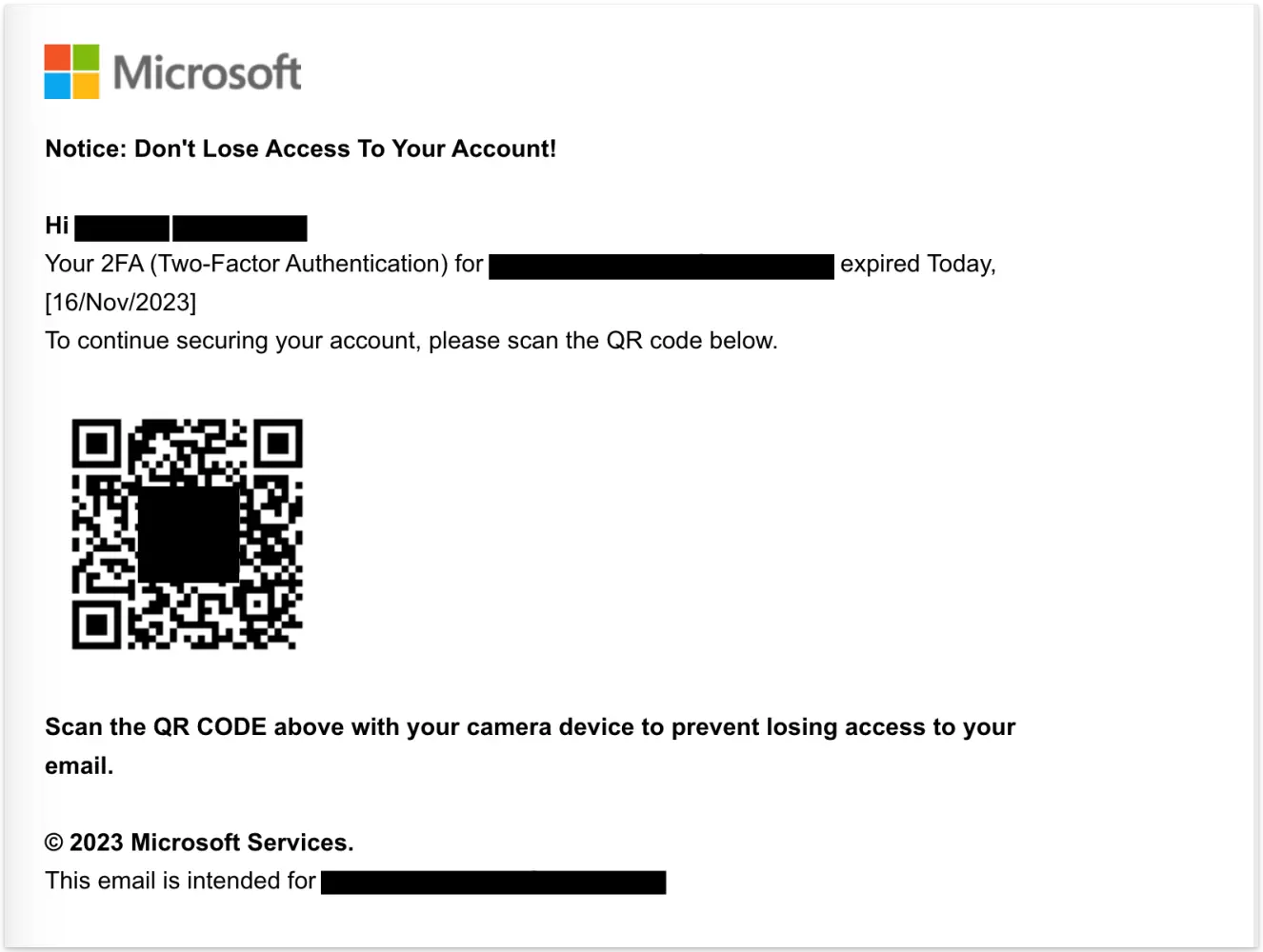
The employee finds it quite authentic and obeys the message with their phone. A Microsoft 365 login page opens up, and they sign in.
Table of Contents
ToggleJust a few minutes, and credential theft is complete. Now, the attackers have access to the company’s email systems, and are all free to snooping, exfiltrating, and pivoting.
This is what QR code phishing or quishing is; it may be referred to as a modern version of phishing that uses QR codes to exploit user behaviors. It is dangerous, effective, and the scariest part is that it is spreading quickly.
What is QR Code Phishing (Quishing)?
A form of cyberattack where the attackers send QR codes via emails, and once the victims scan the codes, they are redirected to fake login pages, credential harvesting sites, or malware-laced downloads is referred to as QR code phishing.
In this type of attack, the malicious link is encoded in the QR code, and so it easily bypasses the traditional email filters or security setups, as these are used for the inspection of plain-text URLs. The exploitation of trust using QR technology is what quishing email attacks do, and it also takes advantage of the scenario of becoming more dependent on mobile devices with every passing day.
Tactic | Why It Works |
Visual Opacity | Users can’t inspect the destination URL of a QR code before scanning. |
Trust Bias | QR codes are seen as helpful tools, not threats. |
Mobile Scanning | Most scans happen on personal smartphones that lack endpoint protection. |
Impersonation | Phishing pages mimic trusted brands: Microsoft, Google, Okta, etc. |
Emotional Manipulation | Attackers use urgency, fear, and deadlines to provoke quick reactions. |
From restaurant menus and event check-ins to software logins to payment systems, QR codes are everywhere now. So, when it comes to QR codes, we often perceive them to be legitimate. QR codes have become so common now that users are no longer giving a second thought before scanning.
This is what the attackers are taking advantage of.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
How Traditional Email Security Falls Short
Yes, there have been some advances in phishing detection. However, when it comes to phishing with QR codes, there are some serious blind spots in security infrastructure. Have a look at the drawbacks now:
- As the QR codes are image-based, link scanners are not able to “see” or decode them.
- It involves mobile-based access, and this makes detection difficult, as most email security tools are active only on desktops.
- Security tools often fail to analyze user intent. It may happen that a QR code is benign on the surface, but the destination is weaponized later.
- QR scam awareness training doesn’t deal with visual payloads, as almost all phishing training programmes put their focus on text and link manipulation.
The scanning device is out of scope for logging and EDR, and for this reason, the security teams get to know about the security breach long after the damage has been done, and this is what makes quishing more dangerous.
Why Quishing Is Especially Dangerous
- When it comes to the devices being used, it is our personal smartphones. So when users scan the QR codes on these devices, it is extremely dangerous, as it lacks the necessary security tools, corporate VPNs, or web filtering.
- In mobile-initiated scans, the security teams face a hard time tracing the attack vendor. So, the credential breach is more scary in QR code scams.
- The attackers steal the credentials on a phone, but these can be easily used by them to access the corporate resources on a desktop. This multi-surface compromise makes quishing more dangerous.
- QRs can easily pass through email gateways, as they are clean payloads, until the victim scans it.
AAPE Defense Framework: How Threatcop Counters Quishing
This threat of QR code phishing is rising at an alarming rate, and it is high time to come up with an effective solution. Threatcop brings some relief with the AAPE Framework, which is a layered Zero Trust approach to simulate, educate, prevent, and respond.
1. Assess – Simulate QR Phishing with TSAT
Threatcop’s TSAT (Security Awareness Tool) allows organizations to conduct multi-attack vector simulations, creating the conditions under which users are most likely to fail and learn.
Here, you can launch QR-based simulations using:
- Fake invoice access pages
- Microsoft 365 login portals
- Secure Dropbox document previews
- Payment verification links
You can collect data on:
- Who scanned the QR
- Device type (if known)
- Whether the user reported the attempt
- Time taken to engage
All these insights allow risk segmentation by team, region, or role.
Visit the TSAT Product Page to know more.
2. Aware – Behavioral Training via TLMS
Just-in-time training modules are crucial here, and Threatcop’s TLMS (Threatcop Learning Management System) proves to be quite effective.
Let’s have a look at what the modules include:
- Multiple content categories
- Role-based training
- Gamified security awareness
Turning user education into organizational muscle memory is what TLMS aims for.
Visit the TLMS Product Page now!
3. Protect – Strengthen Email Authenticity with TDMARC
It often happens that spoofed senders posing as an HR, IT, or Finance team member launch the QR phishing campaigns.
In such cases, TDMARC can provide protection by:
- Protecting outbound email workflow.
- Blocking unauthorized use of your domain
- Enforcing domain alignment through SPF and DKIM
- Monitoring email authentication failures
- Providing real-time alerts on attempted domain abuse
This works wonders by reducing the success rate of QR-based payloads that rely on sender impersonation. And the plus point is the TDMARC reports also show patterns, like a rise in spoofing attempts linked with QR code phishing.
Visit the TDMARC Product Page for more details.
4. Empower – User Reporting with TPIR
An easy way to report suspicious QR codes, even those scanned from personal devices can be quite helpful in preventing such attacks. And this is exactly what Threatcop’s TPIR (Phishing Incident Responder) does, and the employees are now equipped with a quite effective reporting tool.
Let’s have a look at the features now:
- Report phishing directly from email client
- Upload or screenshot suspicious QR codes
- Alert SOC teams with enriched metadata
- Categorize incidents for follow-up investigation
Visit the TPIR Product Page to know more about how it works.
Red Flags Checklist: Spotting Quishing Attempts
Red Flag | Risk Signal |
QR code in unsolicited email | Suspicious method for redirection |
No clickable link; QR only | Prevents link hover-preview |
Urgent or fear-based language | Psychological manipulation |
Generic sender name or email | Likely spoofed domain |
Financial topics like “invoice,” “payment,” “renewal” | Common BEC bait |
Bonus: Quishing Simulation Campaign Tips
Check out some campaign ideas:
- “Scan to reset your Microsoft 365 password.”
- “Verify your timesheet via QR code.”
- “IT notice: MFA update required, scan below.”
- “Internal app update: Scan to install”
Now here are the metrics to track:
- Time from delivery to scan
- Number of users who scan vs. report
- Devices used (desktop-only, mobile-only)
- Common failure patterns by department
You must aim to run these quarterly and keep changing themes to avoid predictability. Most importantly, don’t miss out on including the executive and IT teams, as they are the most common targets.
Final Thoughts: QR Codes as an Emerging Attack Surface
Now that you have got an idea of what QR code phishing is, you are already aware of how dangerous it can be. It is high time the security teams of organizations start treating quishing as a first-class threat vector. The solution lies in:
- Training users on visual payloads
- Running a realistic QR phishing simulation
- Enforcing strong sender identity controls
- Equipping users with fast, intuitive reporting tools
The attacks are evolving rapidly; the inbox is no longer the target, but the camera is. But panic is never the solution; there are cybersecurity experts to help you out. Get in touch today!
Co-Founder & COO at Threatcop
Department: Operations and Marketing
Dip Jung Thapa, Chief Operating Officer (COO) of Threatcop, a leading cybersecurity company dedicated to enhancing people security management for businesses. With a profound understanding of cybersecurity issues, Dip plays a pivotal role in driving Threatcop’s mission to safeguard people’s digital lives.
Co-Founder & COO at Threatcop Department: Operations and Marketing Dip Jung Thapa, Chief Operating Officer (COO) of Threatcop, a leading cybersecurity company dedicated to enhancing people security management for businesses. With a profound understanding of cybersecurity issues, Dip plays a pivotal role in driving Threatcop's mission to safeguard people's digital lives.
