Ransomware is the most destructive kind of cyber attack due to the massive financial losses it inflicts on organisations worldwide. According to IBM, on average, it takes 280 days to detect any threats in the system. For this reason, experts have always advocated that threat hunting-led ransomware detection and prevention must be rigorously and actively carried out.
Table of Contents
ToggleSubscribe to Our Newsletter On Linkedin
Sign up to Stay Tuned with the Latest Cyber Security News and Updates
It is very important to employ threat hunting tools to detect any cyber attacks that may take place in your organization. Most of the security agencies such as the FBI (Federal Bureau of Investigation), NSA (National Security Agency) and CISA (Cybersecurity Infrastructure Security Agency) emphasize the need for organisations to incorporate proactive threat hunting in their cybersecurity framework.
What is Threat Hunting?
Threat hunting refers to the process of proactive analysis to identify cyber threats that might be sneaking around an organization’s infrastructure. The procedure of threat hunting involves deep analysis and monitoring of all the devices and data on the network and seeking malicious actors who might have broken primary security defences.
Threat hunting is becoming a part of a crucial strategy to strengthen the defence of an organization. Cybercriminals persistently attempt to evade being detected while exploiting unauthorized access to an organization’s infrastructure. Thus, threat hunting provides a comprehensive set of tools and services to strengthen the cybersecurity of an organization.

What is Ransomware Detection?
Ransomware has an immensely adverse impact on the finance and reputation of the victim company. In these attacks, cybercriminals hold massive amounts of sensitive data hostage and ask for huge ransoms in return for keeping the data private and giving it back. Many ransomware gangs have gained popularity for launching devastating ransomware attacks on organizations globally.
The significance of ransomware detection is to implement tools and services that could identify potential threats to an organization. Further when an attack occurs, the necessary procedure is carried out to retrieve the lost data without paying a ransom. Another important element that is considered while ransomware detection is malware detection because it is the primary attack vector for ransomware attacks.
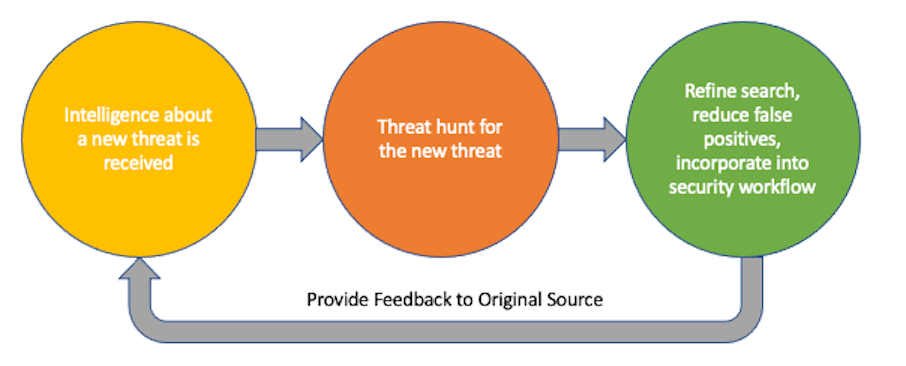
Relevance of Ranomware Detection in Threat Hunting
The procedure of proactively detecting malware and preventing it from entering an organization’s network is one of the prime applications of threat hunting. Ransomware attacks are highly disruptive as they bypass security systems at all levels to reach confidential databases. Thus, threat hunting uses the techniques of ransomware detection to prevent these attacks from happening in the first place.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
How is Ransomware Threat Hunting Done?
Ransomware detection is carried out comprehensively through threat hunting. The historical data of attacks is present in the form of threat intelligence. Thus, threat intelligence helps in developing tools that have some parametric attributes such as deep feature extractor, multi-class classifier, etc. These attributes are used to set out a procedure of threat hunting for ransomware detection.
In addition, threat intelligence is also used to develop hypotheses, which helps in predicting threats. Thus, a defence mechanism is integrated in the cyber security infrastructure to detect malware that could lead to a ransomware attack. There is some specific set of methodologies for ransomware detection, which are built upon the concept of threat hunting.
Techniques of Ransomware Detection through Threat Hunting
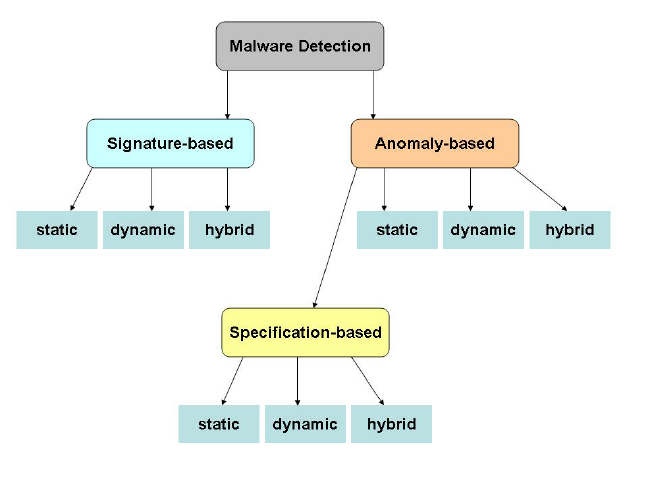
Threat hunting is a continuous process of looking for threats and the collected information is incorporated into the existing security frameworks. Ransomware threat hunting involves a mixed process of malware analysis and automation. Cybercriminals often hide their attack scripts in the malware software. There is a categorical umbrella of techniques that are used for ransomware/malware detection. The three types of detection techniques are :
Signature-based Ransomware Detection
In this threat hunting procedure, the hash value of ransomware samples is compared with known signatures. This provides a quick and static analysis of the system. It is the first level of defence.
Behaviour-based Detection Method
Behavioral understanding of attackers is important to develop hypotheses. In this method, historical data and attack vectors are recorded to provide information on the Indicators of Compromise (IOCs). This method compares IOCs to the average behavioural baseline. There are three major methods for comparing the detected behaviour with baseline.
Traffic Analysis: The threat hunters examine the traffic of the network and its connections. The volume of data transmission and its sources are also analysed. They try to identify off-site servers and ransomware decryption keys. This method requires immense time for analysis and it can sometimes yield false positives.
File System Changes: This method is useful to detect abnormal file executions and multiple renaming. When there is a surge in multiple executions in a day, it is a cause for alarm. Files containing ransomware scripts can stay in the system for a long period without being executed. Threat hunters look for the creation of a file that has larger entropy than the original file. They also observe the enumeration and encryption of such files.
API Calls: This method requires examination of the API calls. This means that it checks the commands that are being executed by the files.
Deception-based Detection
This technique is based on tricking and baiting attackers. This is carried out using a false server or file repository which is not normally used by users.

‘Proactive’ is the Key to Detection and Hunting
Threat hunting and ransomware detection are part of an essential proactive defence strategy. It means an organization can be defended against every kind of attack. The crucial element of defence is comprehending all the possibilities of attack and developing a defence mechanism. There are two fundamental points of contact for landing any cyber attack. One is a machine and the second is human.
Machines can be defended using firewalls, antivirus, antimalware, email gateways, etc. but humans are the leading cause of cyber attacks. About 96% of all cyber attacks are caused by human negligence. To ensure threat hunting and ransomware detection, every organization should carry out Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) to identify all the vulnerabilities and loopholes within the organization’s cyber infrastructure. They must empower and educate their employees to become proactive and prevent phishing, smishing, vishing, etc. using security awareness training (ThreatCop) and threat phishing incident response (TPIR). Cybersecurity is the domain of information technology that is meant to secure digital infrastructure and safeguard the cyber world.
Senior Writer
Shantanu is an accomplished content strategist and technology enthusiast at Threatcop Inc. With a knack for translating technical intricacies into reader-friendly narratives, Shantanu contributes to making cybersecurity insights both informative and enjoyable for tech enthusiasts and general audiences alike.
Senior Writer Shantanu is an accomplished content strategist and technology enthusiast at Threatcop Inc. With a knack for translating technical intricacies into reader-friendly narratives, Shantanu contributes to making cybersecurity insights both informative and enjoyable for tech enthusiasts and general audiences alike.
