The Nobelium group came to light when Microsoft notified them on their website. At the end of December 2020, a series of advanced cyber attacks occurred on Solarwinds Corporation. Russian hackers are notorious and have been accused of carrying out highly sophisticated cyber attacks.
Table of Contents
ToggleAccording to Microsoft, in May 2021, the Nobelium hacker group campaign targeted 140 companies, among which 14 confirmed cases of compromise were noted.
The cyber attacks by the Nobelium group were first identified by Microsoft Corporation. The company regarded this organization as an advanced persistent group (ATP), which targets network and cloud service providers through piggybacking.
Who is the Nobelium Group?
The Nobelium group is a notorious cybercriminal group that is believed to be backed by Russian state agencies. This group uses the ‘supply chain attack’ as the primary attack vector, which they have used to target around 140 technology companies in the global information technology supply chain.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
Nobelium carried out the breach by infecting Orion software’s update. This update was deployed to around 18000 customers. Further, they targeted numerous high-profile companies and agencies such as Microsoft, US Treasury, Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA), Department of Justice (DOJ), etc. The hacker group infected the ‘software update’ with malware.
Among all the prime US government agencies, 80% of the emails from the Department of Justice were compromised.
However, Microsoft believed that this level of attack would have taken 1000 hackers to execute. The group is believed to carry out attacks through phishing, spray-and-pray credential stuffing, token theft, abusing APIs, etc.
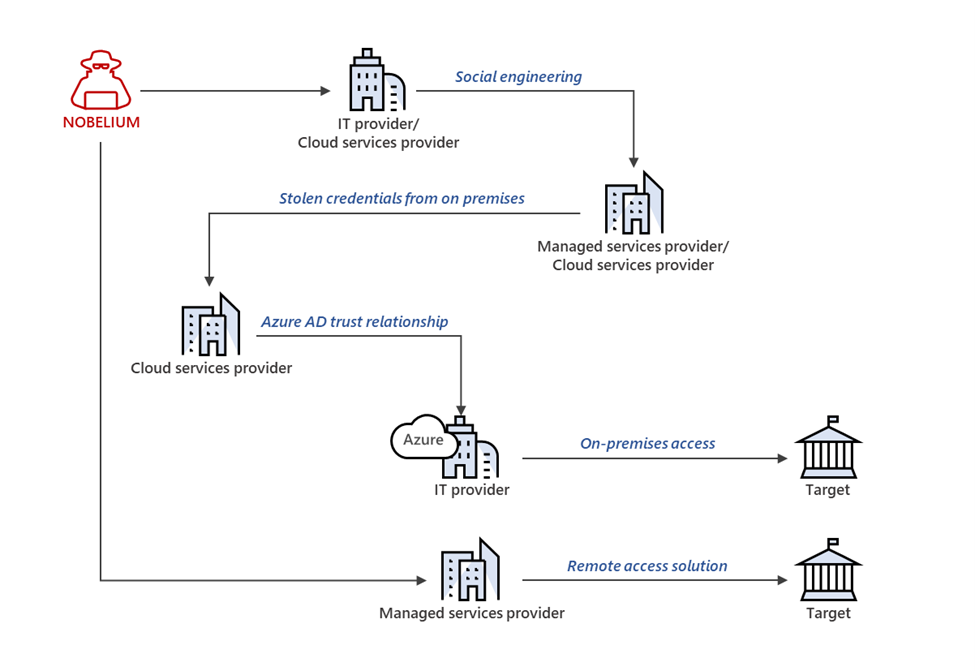
What Happened at SolarWinds Corporation?
Nobelium is the Russian cybercriminal group that infected a software named Orion. Then they injected it into the systems of SolarWinds Corporation through supply chain attacks, along with many other companies. The threat actors infected the software, which was provided by the SolarWinds company. This is how they targeted the customers of SolarWinds Corp.
SolarWinds Corporation is a software company that provides system management and technical services to various organizations globally. These services are meant to manage the infrastructure and monitor the network. Orion was an IT performance management system that had access to thousands of networks of customers.
The Nobelium hackers group inserted a malicious code into the Orion network management system, which was used by numerous government agencies and multinational companies globally. Due to the addition of this malicious code, the Orion Platform created a backdoor. This allowed the hackers to access accounts and impersonate users of victim organizations.
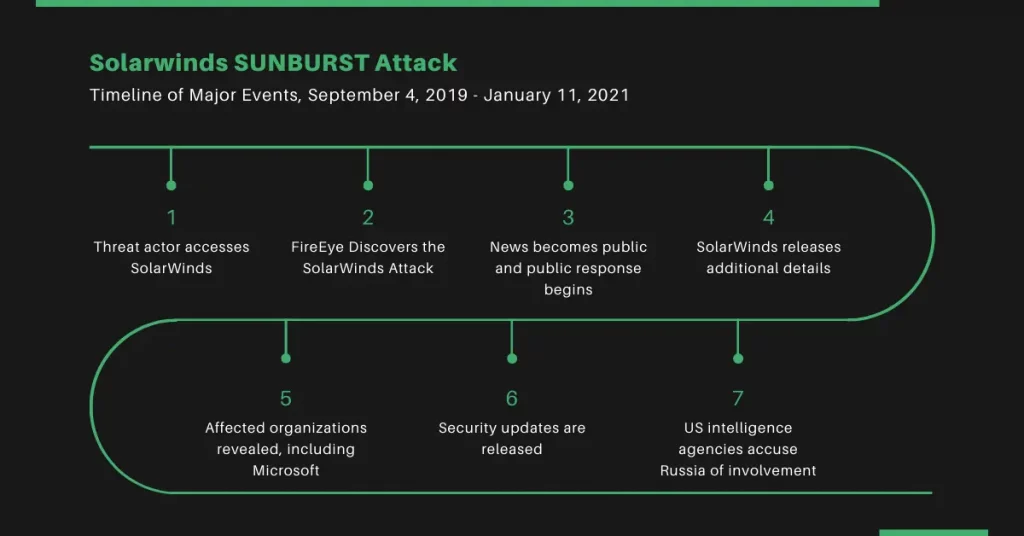
Timeline of the Attack
Below is the list of dates on which a major activity has taken place.
- 4th September 2019: Russian hackers get access to SolarWinds Corporation.
- 12th September 2019: The hackers injected the test code and performed a trial run. They employed a ‘sophisticated injection source’ for inserting the SUNBURST malicious code into the Orion Platform software.
- 20th February 2020: The hackers compiled and deployed the SUNBURST attack.
- 4th June 2020: The hackers removed the SUNBURST malicious code from SolarWinds systems.
- 8th December 2020: FireEye, a cyber security company, uncovered a breach in its systems and launched an investigation.
- 12th December 2020: FireEye discloses that the breach was a result of a cyber attack on SolarWinds’ Orion Platform.
- 15th December 2020: SolarWinds released a software fix.
How was Nobelium Caught?
FireEye is a company that first identified the breach and notified people globally. Then Microsoft took the initiative to explore the extent of the attack. The infected software implanted by Nobelium remained undetected up to December 2020. Then, Microsoft released a series of technical guidelines to take precautionary measures for the customers.
However, Microsoft stated that the responsible group or individuals remained in dark until January 2021, when the US Intelligence Agency accused the Russian state of sponsoring the attack. From July to mid-October, threat actors attacked 609 customers around 22,868 times, while in three years, Microsoft has notified customers about state-sponsored cyber attacks around 20,500 times.
State-sponsored Cyber Attacks
Nation-state cyber attacks are considered some of the most malicious and dangerous. These attacks are carried out in the interest of a host country to damage the target nation. Some of the state-sponsored hackers groups are:
- Cozy Bear (allegedly state-sponsored by Russia)
- Lazarus Group (allegedly state-sponsored by North Korea)
- Double Dragon (allegedly state-sponsored by China)
- Fancy Bear (allegedly state-sponsored by Russia)
- Nobelium (allegedly state-sponsored by Russia)
The purpose of state-sponsored cyber attacks is to target the critical infrastructure, think tanks, and government agencies of other countries. So, every organization keeps on improving its cyber infrastructure to defend against such attacks, and at the same time, threat actors develop sophisticated methods to carry out attacks.
Among all the kinds of cyber attacks, malware-based attacks are the most common. For example ransomware attacks. Some affiliates (an entity that facilitates attacks) have developed a business model-based ransomware attack. They employ hacker groups to carry out the designated attacks. They provide a service to clients, who want to lay cyber attacks on any other organization. This approach is known as “Ransomware as a Service Attack”.
Read more about Ransomware as a Service Attack
How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks?
Most ransomware attacks are carried out through email spamming or email spoofing. Those emails are meant to lure the target to click on a link to a phishing website, where they are asked to provide credentials. This is how they lose their credentials. Secondly, these emails might contain malware that could lead to a data breach or network breach.
Thus, one could say that ransomware attacks occur mostly due to human negligence. That’s why it is very important to employ tools to safeguard email servers and networks. Along with that, organizations need to train their employees in security awareness, so that they can identify how to defend and protect themselves against social engineering attacks.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
To mark Cybersecurity Awareness Month, Threatcop collaborated with 31 respected CISOs and CTOs from prominent organizations. Together, we’re working towards a safer digital future.
Explore Here: 31 Cybersecurity Awareness Ideas from Security Leaders
Security Compliance Executive
Department: Compliance, Threatcop
Sanjana is a Security Compliance Executive working on best-of-the-industry-level compliances relevant from a cybersecurity perspective, their implementation, learning and outcomes in various business domains.
Security Compliance Executive Department: Compliance, Threatcop Sanjana is a Security Compliance Executive working on best-of-the-industry-level compliances relevant from a cybersecurity perspective, their implementation, learning and outcomes in various business domains.
