Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology have taken over the attention of the media in the last couple of years. It can be seen that more and more people are becoming interested in cryptocurrency trading. In the meantime, NFT Scam is rising in the limelight for its immense profitability, apart from cryptocurrency. These NFTs have become a medium for scamming crypto and NFT (Non-Fungible Tokens) enthusiasts nowadays.
Table of Contents
ToggleCryptocurrencies are primarily entangled with an array of scams. There have been numerous cases of scams in the past with NFTs. For example, there was an NFT marketplace by the name of “Evolved Apes” that had 10,000 unique NFTs. The project was associated with a game where these Apes would fight and one of them would prevail. A week after the launch of the project, the game vanished, along with its official website and Twitter account. From the traces, it was found that they drained $2.7 million (798 Ether coins) from users who registered.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter On Linkedin
Sign up to Stay Tuned with the Latest Cyber Security News and Updates
What is NFT Scam?
The foremost element that lures users to buy NFTs is the expectation of profitability from them. As cryptocurrency’s price varies with the fluctuation in the crypto market, the prices of NFTs fluctuate too. So, designers and developers who establish a particular NFT or a whole NFT market can be imitated by scammers to funnel money, which is known as an NFT scam.
Digital artists and NFT creators are creating NFTs that cost somewhere around $50,000 to $60,000 and making millions from them. Scammers and malicious actors attempt to impersonate them or their medium to funnel such a large amount of money to themselves.

How NFT Scam is a Social Engineering Attack?
The notion of social engineering tactics used in the NFT scam is that each NFT is created with the objective of increasing its value. Prices in the domain of blockchain tokens fluctuate based on their quantity and demand in the market.
Scammers use tactics like forging and popularizing a specific Non-Fungible Token. And when such tokens become overvalued or overbought, the scammer nullifies all the domains of websites or social media accounts where those tokens were populated.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
What are Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)?
NFTs are digital assets that are based on blockchain technology to keep a record of ownership of any object. This object can be an image, a game item, a video, etc. It is a non-interchangeable unit of data that is stored in a digital ledger that is encrypted. The most popular usage of NFT is that it is used as a public digital ledger to issue a “certificate of authenticity.“
NFTs have become a multi-billion dollar sector of the crypto industry, gaining a lot of attention and popularity. There were several items that had attained prices of over $30,000. The selling proposition of NFT is that it utilizes blockchain technology to establish an indelible digital record.

What is Blockchain Technology?
A blockchain is a type of distributed database that is shared across the nodes of the network. As a database, they record information in the form of a digital ledger. The popularity of this technology came with the existence of Bitcoin, which was first formed for the purpose of securing and decentralizing transaction records.
NFT Scam Using Blockchain Technology
The application of the blockchain is to provide an encrypted stream of blocks that can be used as non-fungible tokens. Scammers use this token to generate fake NFTs, which they use to popularize using other multiple mediums. They use websites and social media websites to popularize those tokens and scam users.
Common NFT Scams
Several mediums lead to NFT scams. Among them, phishing is a conceptual medium, and others are fake NFT websites, fake offers, giveaway scams, etc.
1. Phishing Scams
It is one of the most common forms of social engineering attack. Scammers send out emails posing themselves as famous NFT website and lure them into offers. Such emails usually ask users to click on an embedded link that takes a user to a phishing website. These websites record the link and credentials to your wallet. Scammers use them to wipe out every cent from it.
2. Fake NFT Websites & Social Media Accounts
Whoever gets interested in NFT seeks websites where they can buy and sell them. There are numerous websites and online resources about NFT, and many of them are fake. These websites look like genuine websites but it’s there so that you can make at least one purchase. Once the scammers have all the credentials and MetaMask wallet addresses, they steal all the available cryptocurrency.
These websites or marketplaces also require social media accounts to popularise them. So, mainly Twitter and Telegram social media accounts are created to develop a reputation among the users. For example, MetaBirkins NFT on the OpenSea website was sold for $42,000 and was replicated from the Hermes website. They also have an Instagram account for MetaBirkins NFT that helped them in popularising the NFT.
3. Impersonation
Impersonation is one of the intrigued mediums of carrying out the NFT scam which lures most of the people out there. There are mainly two types of impersonation that are carried out by NFT scammers given below.
- Artist Impersonation: It is one of the most common NFT scams that involve scammers presenting themselves as some artist. Scammers easily commit digital art theft and portray it as it is theirs. Further, they attempt to sell such popular NFTs at a very low price. This allows them to make a few successful sales after which they terminate the impersonated account. For example, Rarible.com replicas on Telegram.
- In another scenario, a digital artist name Milos Rajkovic reported that his 122 images have been impersonated. These images were put on sale for a total worth $50,000 on OpenSea.
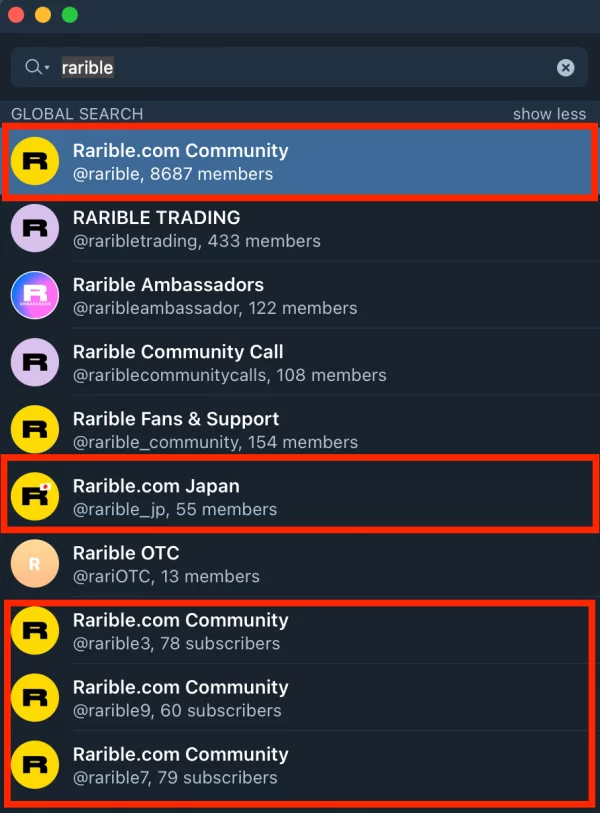
- Brand Impersonation: This has been a more common form of impersonation scam that is prevalent in cryptocurrencies. The scammers usually create an account that is similar to a particular brand. They exploit the popularity of the brand and make several sales for their own profitability. In one case, an NFT collector, Jeff Nicholas, was targeted and his wallet was wiped out, incurring him a loss of $480,000.
4. Fake NFT Stores
In this kind of NFT scam, the threat actors often create a fake store that is similar to some popular marketplace. The impact of such fake stores is that people often make purchases but they never receive any allocation. For example, some NFT scammers have created a fake marketplace just like OpenSea to carry out their targeted activities. In one scam, an NFT known as ApeGang was priced at $39,428.10 (10 ETH at the time).
5. Replica Scams
The impersonation and fake stores can be considered as a type of replica scam. But in this one specifically, the digital art and object, whose NFTs are created are replicated. It means a scammer copies some genuine art and claims it as its own. For example, in 2021 there were several registrations of domains with names like Rarible, Audius, Opensea, etc., that have replicated genuine marketplaces or NFTs.

6. Fake Offers or Giveaways
The primary target of an NFT scammer is crypto enthusiasts. They are more interested in targeting people who are already associated with blockchain technology. They carry out scams by promising them free NFTs or crypto coins related to a particular NFT market. Sometimes, these scammers launch a project where they promise to airdrop or giveaway after a certain period of time and after making certain purchases of NFTs.
The Dark Web and the NFT Scam
Several marketplaces and NFT stores are available on the dark web too. According to an article from the Indian Express, Ross Ulbricht founded a marketplace on the dark web by the name of Silk Road. He sold an NFT of a pencil sketch that was titled ‘Perspective’ at a price of $6.2 million, which was overpriced. He was later convicted of a slew of illegal operations on Slik Road.
This is a popular example of how the dark web is coming under the radar for carrying out NFT scams. Scammers are looking for opportunities to carry out targeted activities aimed at popularising a particular faked or impersonated NFT.
How to Avoid NFT Scam?
- One must avoid providing personal information and credentials for digital wallets in pop-ups or ads on any NFT website.
- Make sure to verify the contact address of any NFT with the creator’s website.
- Use a couple of free tools online to scan a website for its legitimacy.
- Make sure to check the historical record of the wallet associated with the NFT project before making an investment.
- Don’t get trapped in the marketing of social media influencers and conduct your own research on a particular NFT project.
- One can seek other investors in the same project and communicate with them for their opinion.
- One must double-check the currency of the NFT trade to avoid bidding scams.
- Avoid using third-party customer support and always choose the official website’s customer service.
- One must always check and verify the offers or giveaways that can be categorized under ‘too good to be true.’
The Ultimate Goal is to Become Aware and Avoid NFT Scams
Since the NFT market is still in its budding phase, it is bound to attract a lot of attention. With the promising notion of huge profit, it will continue to attract scammers and threat actors. The most vigilant method of ensuring defense against NFT scams is by keeping oneself updated, aware, and connected with similar NFT enthusiasts.
Self-education and research are prominent in the blockchain technology-based industry. But there will be a time when one reaches the end of the line, and then they must look out for experienced creators and collectors. The most educated decision will be to stay alert to secure your investment and make minimum losses.
