Email communication has long been a cornerstone of modern business and personal interactions. However, with the rising sophistication of cyber threats and the increasing importance of data security, it has become crucial to revisit and reinforce the security measures that govern email communications. The recent introduction of new anti spam guidelines focuses on Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) underscores a significant shift in email security protocols, emphasizing the need for robust mechanisms to combat email fraud and phishing attempts.
Table of Contents
ToggleWith the surge in outbound email activities, especially in bulk email practices, businesses face a dual challenge – maintaining domain reputation and ensuring email deliverability. Recent data reveals startling figures in this context: according to DMARC.org, a mere 14% of global domains have strong enforcement policies. Furthermore, a report by Scalelab highlights that an average of 20.4% of emails either end up in spam or remain undelivered. This article explores the underlying issues and delves into these guidelines, underscoring their importance in fortifying email systems against prevalent threats.
New DMARC Guidelines: A Helping Hand for CISOs
In a pivotal move to bolster email security and domain integrity, tech giants like Yahoo and Google have recently implemented stringent DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) policies. These new guidelines represent a significant shift in the approach to email authentication, aiming to combat phishing, spoofing, and other email-based threats more effectively.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
Google & Yahoo’s New Anti Spam Policy: A Stricter Stance on Authentication
Google has adopted a more stringent DMARC policy that mandates the authentication of outgoing emails using specific standards. Under this policy, emails failing to pass SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) checks will be subject to rejection or quarantine. This robust stance necessitates organizations to configure their email systems meticulously, ensuring that their emails are authenticated at the domain level to prevent being marked as spam or rejected outright.

Key Highlights from the Guidelines
- Updated requirements include the use of a Transport Layer Security (TLS) connection for transmitting emails.
- Senders must set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for domain authentication.
- Sending IP addresses must have a PTR record associating the hostname with the IP address.
- Include one-click unsubscribe for marketing messages exceeding 5,000 per day.
- Follow the Internet Format Standard (RFC 5322) and HTML standards for message formatting.
- Keep spam rates below 0.10% and avoid reaching 0.30% or higher for better resilience.
Read More: New Gmail protections for a safer, less spammy inbox
Sending Guidelines: Do’s & Don’ts of Mailing Practices
Authentication
Authenticate email with aligned SPF and DKIM. Verify that your email provider supports this.
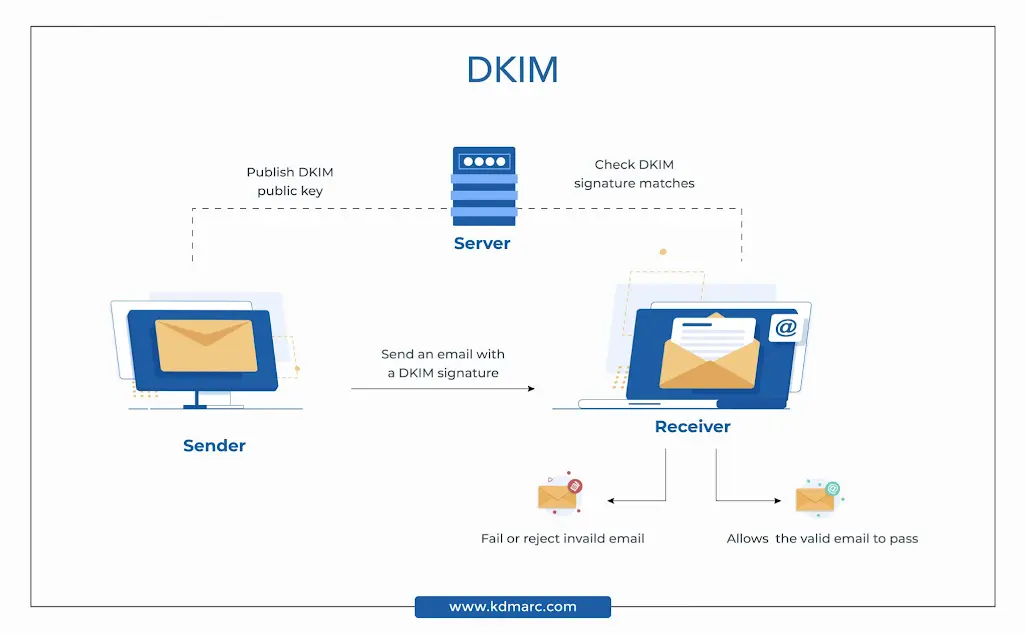
Sender IP Address
Ideally, send all messages from the same IP address. Use different IP addresses for distinct message types (e.g., account notifications, promotional messages).
Consistent From: Addresses
Maintain consistency in the From: email address for messages of the same category, enhancing recognition and reducing spam likelihood.
Example:
- Sales receipt messages: [email protected]
- Promotional messages: [email protected]
- Account notification messages: [email protected]
Recipient Contacts
Messages sent from addresses in the recipient’s contacts are less likely to be marked as spam.
Avoid Mixing Content
Refrain from combining different types of content within the same message, such as including promotions in sales receipt messages.
Avoid Spoofing
Do not impersonate other domains or senders without permission (spoofing), as Gmail may mark these messages as spam.
Internal Messages
Avoid marking internal messages as spam to prevent negative impacts on your domain’s reputation.
Avoid Purchased Email Lists
Do not purchase email addresses from other companies, as this can lead to spam markings.
Permission-based Sending
Send messages only to those who have signed up to receive them. Avoid sending to non-subscribers to prevent spam reports.
Opt-in Forms
Be cautious with opt-in forms. Ensure they are not checked by default, and do not automatically subscribe to users without explicit consent.
Recipient Feedback
Acknowledge that some legitimate messages may be marked as spam. Encourage recipients to mark valid messages as not spam for improved future delivery to their inbox.
Impact on Security Leaders and Organizations
For Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and security leaders, these new guidelines from Yahoo and Google serve as a clarion call to reassess and reinforce their organizations’ email security protocols. Adhering to these DMARC policies not only enhances an organization’s email deliverability but also fortifies its reputation by minimizing the risk of domain spoofing and phishing attacks.
CISOs play a crucial role in advancing DMARC policies within their organizations. They are responsible for educating their teams about the importance of email authentication and ensuring that the organization’s email security strategies are in line with the latest DMARC standards.
Implementing these measures requires a careful configuration of email servers, ensuring compliance with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC standards. By doing so, organizations can expect a significant reduction in the misuse of their email domains, safeguarding their communication channels and bolstering their cybersecurity posture.
Know More: Implement DMARC to Ensure Email Security
The Role of DMARC in People Security
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) is a crucial protocol for verifying sender authenticity, making it harder for cybercriminals to exploit email systems. DMARC works in conjunction with two other key authentication protocols – Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM). These protocols collectively help in establishing a secure email environment by preventing domain impersonation and email spoofing.
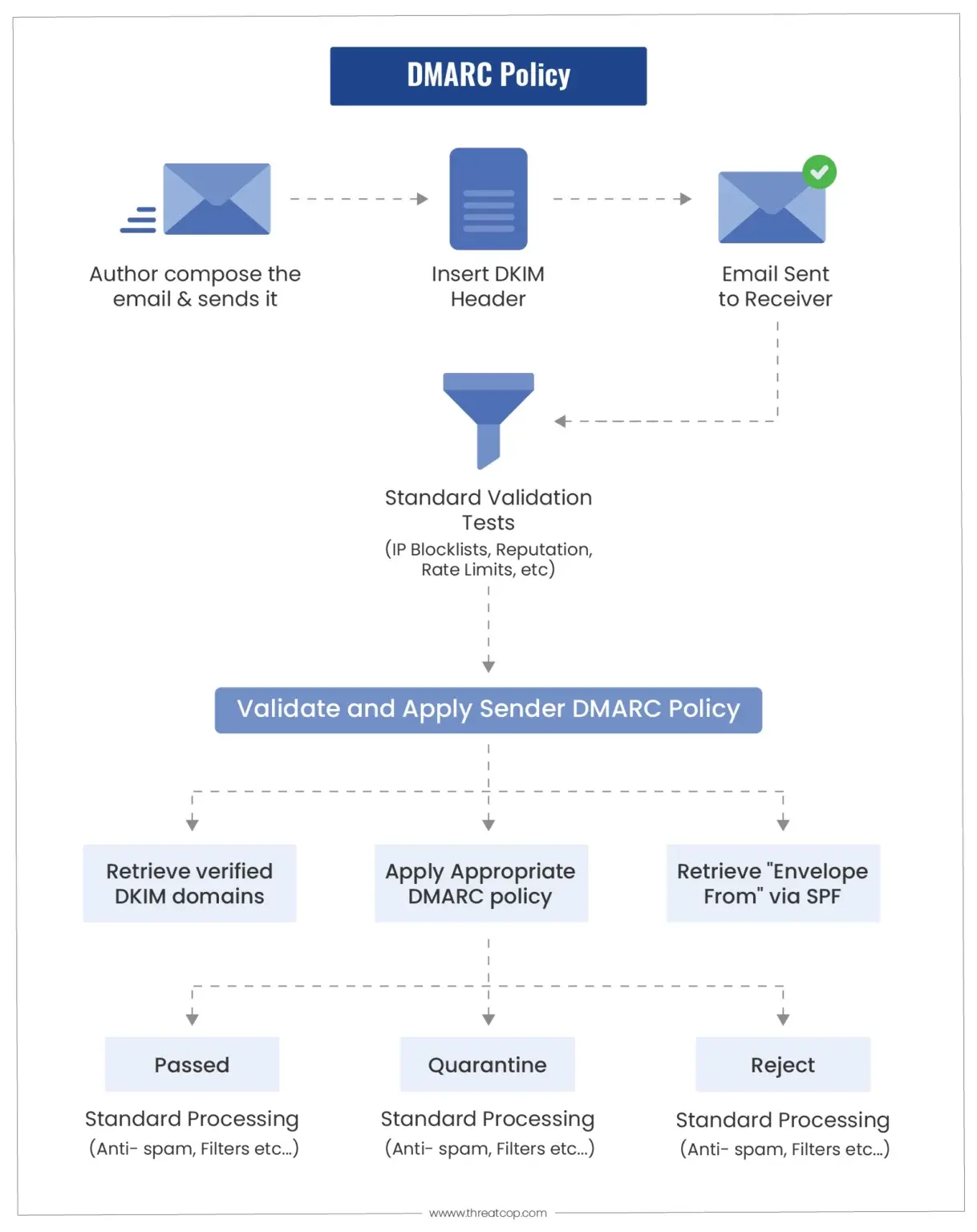
Enhancing Email Authentication: DMARC is an email authentication protocol that builds upon SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). It ensures that the email sender is legitimate and authorized by the domain owner.
Preventing Email Spoofing and Phishing: DMARC helps in preventing bad actors from using a company’s domain to send fraudulent emails. This significantly reduces the risk of phishing attacks.
Improving Email Deliverability: By establishing a domain’s authenticity, DMARC can improve the deliverability of bulk emails. Emails authenticated via DMARC are less likely to be flagged as spam, ensuring they reach their intended recipients.
Maintaining Domain Reputation: DMARC helps in maintaining and enhancing a domain’s reputation by preventing its misuse. A good domain reputation improves email deliverability rates and the effectiveness of email marketing campaigns.
Compliance with New Guidelines and Regulations: Many modern data protection regulations and guidelines recommend or require the use of DMARC to secure email communications. Implementing DMARC can help businesses stay compliant with these regulations.
Reporting and Visibility: DMARC provides insights and reports on email delivery and authentication failures. This data is invaluable for businesses to understand their email ecosystem and make informed decisions to optimize their email strategy.
Key Benefits of Implementing DMARC:
- Prevents Email Spoofing: By authenticating outgoing emails, DMARC ensures that only legitimate emails reach your recipients, thereby preventing email spoofing.
- Enhances Email Deliverability: Proper DMARC configuration boosts your email domain reputation, ensuring high deliverability rates.
- Gains Visibility and Control: DMARC reports give insights into email flows, enabling CISOs to monitor and control email delivery effectively.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards: DMARC helps in complying with various data protection and privacy regulations.
TDMARC: Tailored DMARC Solution for Enhanced Email Security
TDMARC stands as a robust, SaaS-based solution, specifically designed to simplify the configuration and management of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records. It offers a user-friendly dashboard, real-time alerts, and detailed analytics, making it a go-to choice for CISOs seeking to strengthen their organization’s email security posture.
Features of TDMARC:
- Automated SPF and DKIM Configuration: Simplifies the complex process of setting up SPF and DKIM records.
- Real-Time Alerting System: Notifies when unauthorized email sources attempt to use your domain.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Offers detailed insights into email authentication status and potential vulnerabilities.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy-to-navigate dashboard for efficient management of email security protocols.
Also Read: Deploying DMARC? Avoid These 7 Common Mistakes!
Empowering CISOs with TDMARC
TDMARC empowers CISOs to take proactive steps in safeguarding their organization’s email domain. By implementing TDMARC, CISOs can:
- Ensure Secure Email Communications: Secure the integrity of organizational communication channels.
- Prevent Domain Abuse: Stop cybercriminals from misusing the organization’s domain for malicious activities.
- Educate and Inform Stakeholders: Utilize TDMARC’s comprehensive reports to educate stakeholders about email security.
- Align with Best Practices: Stay ahead of emerging threats by aligning with the latest email security best practices.
For CISOs, the implementation of TDMARC is a strategic step towards enhancing email security. It not only protects the organization’s domain from abuse but also builds a strong foundation for trusted email communications. Investing in TDMARC is an investment in the security and reputation of your business.

Technical Content Writer at Threatcop
Ritu Yadav is a seasoned Technical Content Writer at Threatcop, leveraging her extensive experience as a former journalist with leading media organizations. Her expertise bridges the worlds of in-depth research on cybersecurity, delivering informative and engaging content.
Technical Content Writer at Threatcop Ritu Yadav is a seasoned Technical Content Writer at Threatcop, leveraging her extensive experience as a former journalist with leading media organizations. Her expertise bridges the worlds of in-depth research on cybersecurity, delivering informative and engaging content.
