According to a report by Egress Email Security, 69% of organizations reported an increase in phishing attempts in 2024. Hackers use AI-generated phishing emails to trap people, which led to the growth in the share of cyberattacks. Also, 22 % of phishing emails can now bypass the old and traditional Secure Email Gateways (SEGs).
Table of Contents
ToggleDue to a lack of proper email security posture, organizations globally are affected by various types of cyberattacks. Modern attacks like domain spoofing and phishing have become a major threat as hackers use them to deceive people by appearing as legitimate sources.
By using these cyberattacks, hackers can mislead users to click on suspicious links or download malicious files through untrusted email sources. To reduce such email threats, organizations need to understand the importance of email security and apply preventive measures to strengthen email security posture.
In this blog, we will be understanding email security, its importance, benefits and best practices to be future-ready against modern email threats.
What is Email Security?
Email is one of the major components of an organization which is used for internal and external communication as it is a feasible source to send and receive mail.
By its ease and feasibility in nature, it becomes a primary target for hackers which they use to trick employees of an organization for stealing confidential and financial details. To protect the organization from these email threats it’s important to understand the working and need of email security.
In email security, it involves the process in which users and email communications mediums are protected against various cyberattacks and prevented from unauthorized access, data loss or email compromise. Email security helps to protect users from common email threats and aims to ensure the integrity and authenticity of the email.
By strengthening email security organizations can be safe from spoofing, phishing attacks, email frauds, spam, malware and prevent intruders from unauthorized access.
Read About BEC Attacks: A Global Enterprise Concern
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
Types of Email Security Threats
Phishing is a cybercrime where the attacker pretends to be a trustworthy entity to steal sensitive information. Here are the types of security email threats:
- Spear Phishing: Targets an individual with a tailored message. For example, using information derived from social media, an attacker could easily send out a very plausible request “from” a colleague.
- Whaling: The cons target C-level executives (“big fish”) with high value and at stake, such as JSON web tokens as their role and title, using emails that are very important critical business emails.
- Clone Phishing: In this, an email is created with an attachment or a link usually containing “malicious” “content” that is almost “identical” to an “already” existing, legitimate email. For example, remailing a company-wide email with “the”.
- Business Email Compromise: This is a sophisticated fraud focusing on companies that perform wire transfer operations and foreign suppliers.
- CEO Fraud: This is the type of fraud where the criminal impersonating the CEO sends out an email to the employees to transfer money urgently, most times to a supposedly confidential deal.
- False Invoicing Scheme: This is when fraudsters pretend to be real suppliers and request fund transfers for the invoices to a new account.
- Attorney Impersonation: Perpetrators pretend to be lawyers or legal advisors during those sensitive transactions, insisting on quick, confidential payments.
Why is Email Security Important?
Rising cyber threats and lack of security awareness among employees are the major reason due to which organizations need to strengthen email security posture. As organizations are shifting to cloud services it has resulted in increasing attack surface for hackers.
To protect and meet modern needs, email security plays a major role in reducing unauthorized access and preventing confidential details of organizations. Email Security helps to ensure proper security measures and protect against malware, phishing, and data breaches.
Best Practices for Email Security
- To stop intruders from unauthorized access there is a need to ensure that passwords are unique and complex. Also, using Multi-Factor Authentication(MFA) adds an extra layer of security.
- Organizations can use the encryption methodology to stop being intercepted and protect confidential details.
- Employees need to be trained in such a way so that they are able to identify and respond to email threats from untrusted and suspicious sources.
- To detect unusual activities and potential breaches organizations need to use monitoring and detection tools for strengthening security posture.
- Using spam filters can help block malicious and harmful emails and reduce the chances of clicking on unwanted and suspicious emails.
Authentication Protocols
Email Authentication involves some very important protocols that must be observed to ensure the identity of the sender and secure the entire communication done through emails.
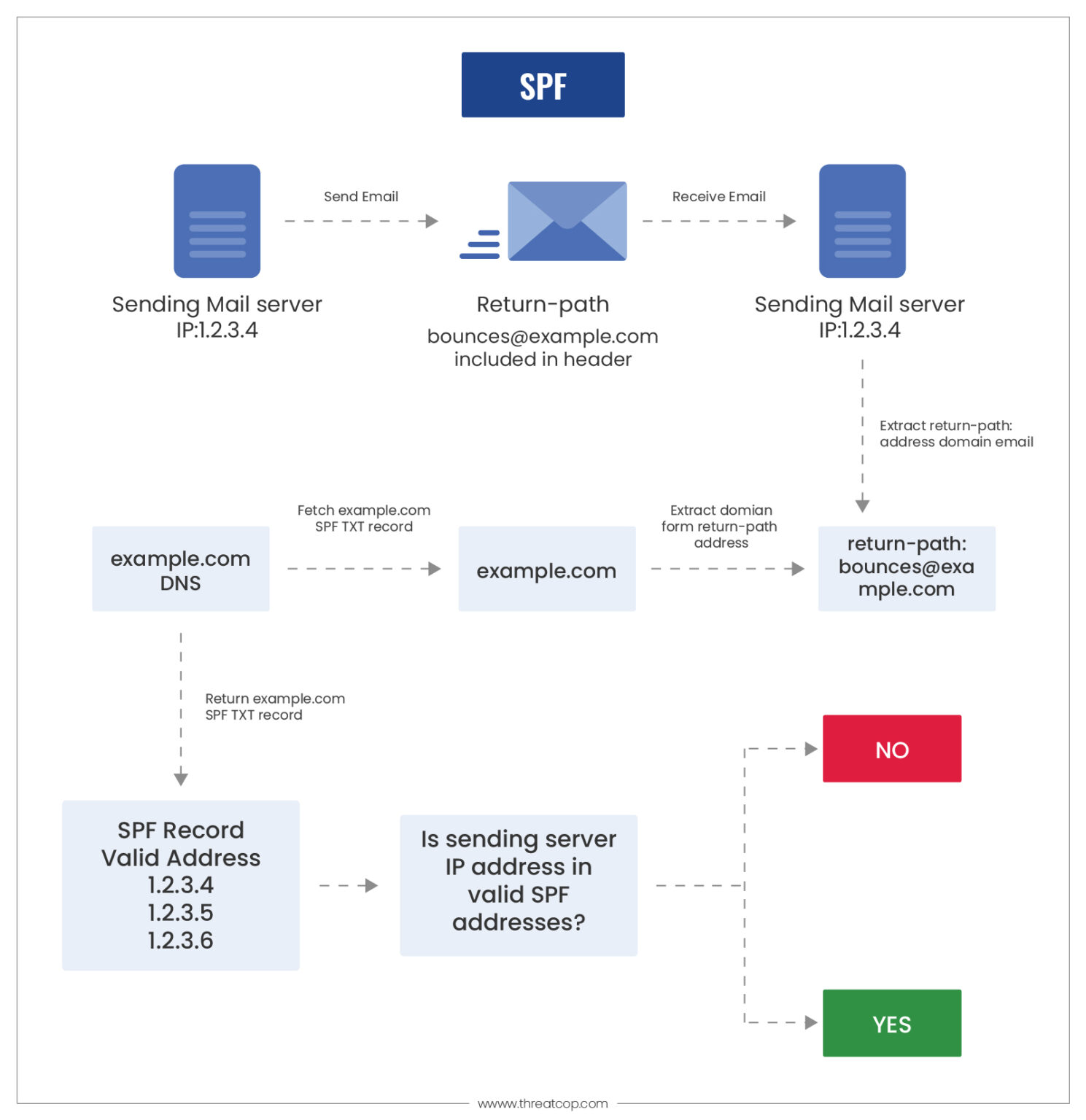
- Sender Policy Framework: This compares the sender’s IP against a list of approved IPs from that domain, hence the validation of the e-mail.
- DomainKeys Identified Mail: This uses a cryptographic signature to trick mail servers that the domain owner sends and authorizes the email.
- Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC): This is a combination of the SPF and DKIM authentication that verifies and reports the validity of a suspicious email.
Implementing Email Authentication Protocols
- Leverage TDMARC: Begin by utilizing a Threat Detection, Reporting, and Conformance (Threatcop DMARC) solution. TDMARC simplifies the implementation and management of email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
- Setup SPF: Set up, in your DNS setup, a record of an SPF entry listing all the authorized mail servers.
- Implement DKIM: Create a unique DKIM key pair and publish the public key in your DNS records.
- Configure DMARC: Generate the DMARC policy for the DNS records to let the receivers know how to handle unauthenticated emails.
- Test our SPF and DKIM: Validate the SPF and DKIM records with a test for the functionality of the available testing tools.
- Monitor DMARC Reports: You receive DMARC reports, and you can monitor them for any unauthorized use of your email and its overall performance.
- Make Adjustments: Update your records from time to time based on organizational changes and practices for sending emails.
- Educate the Stakeholders: Make sure every person involved is enlightened on these protocols and their importance in the security framework for your organization.
Benefits of Email Security in Enhancing Your Security Posture
The following are the advantages that can be achieved through email security:
- Email security helps organizations protect their brand reputation by preventing data breaches and cyber threats.
- It helps to enhance productivity by reducing downtimes and operational disruptions during the scenarios of cyberattacks.
- Organizations can meet security compliances and regulatory requirements and avoid penalties by strengthening email security posture.
- Businesses and Organizations can maintain customer trust by protecting their data and establishing secure communications.
- It also helps in protecting the organization from financial losses which happen through cyber fraud and data theft.
How Threatcop Strengthens Email Security for Organizations
Threatcop has a product known as TDMARC which can help organizations to strengthen their email security and authentication structure. It also helps organizations to protect their outbound email workflow.
Traditional tools just focus on monitoring and visibility, but TDMARC takes it to the next level by using modern technologies to enhance your productivity as well as security posture.
TDMARC offers enhanced features like:- lookalike domain visibility, Smart SPF, Smart Dmarc, SIEM integration, real-time notification, MTA-STS, and Smart BIMI to meet modern email security needs of the organizations and protect them from phishing and spoofing attacks.
Conclusion
Email security is an important aspect of protecting organizations against upcoming cyber threats, meeting regulatory compliances, and enhancing productivity. To reduce the chances of email threats organizations can use modern solutions such as TDMARC for enhancing email security and authentication structure. Training employees is also an important aspect so that they can identify and respond to modern email threats. Using best practices and strengthening email security posture can help to be ready against phishing and spoofing attempts.

Technical Content Writer at Threatcop
Milind Udbhav is a cybersecurity researcher and technology enthusiast. As a Technical Content Writer at Threatcop, he uses his research experience to create informative content which helps audience to understand core concepts easily.
Technical Content Writer at Threatcop Milind Udbhav is a cybersecurity researcher and technology enthusiast. As a Technical Content Writer at Threatcop, he uses his research experience to create informative content which helps audience to understand core concepts easily.
