With the new mandate that is coming into effect from February 2024, there is a heightened focus on the regular updating and rotation of DKIM keys. This directive, issued by leading technology and email service providers, aims to bolster email security further. Regular rotation of DKIM keys is now recognized as a crucial practice for maintaining the integrity and security of email communications. It prevents potential exploits of outdated or compromised keys and ensures continuous effectiveness in email authentication processes.
Table of Contents
ToggleThis updated guideline is particularly pertinent for organizations managing substantial email traffic, as it plays a vital role in safeguarding against evolving email-based cyber threats. Adhering to this mandate not only enhances security measures but also sustains the trust and reliability of organizational email communication channels.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter On Linkedin
Sign up to Stay Tuned with the Latest Cyber Security News and Updates
What is DKIM Key Rotation?
DKIM key rotation refers to the process of changing the DKIM keys periodically. This action requires changing the entire DKIM key or a particular attribute of the DKIM key. This particular attribute is the “p=” tag, which signifies the public key. This public key is a combination of alphabets, numbers, and symbols which is recorded in DNS. The modification of the public key tag can also involve the modification of the key type.
DKIM stands for DomainKeys Identified Mail, whose primary purpose is to digitally sign the emails of a particular domain or email service provider. Read more about DKIM and its significance.
How Does DKIM Key Rotation Prevent DKIM Vulnerability?
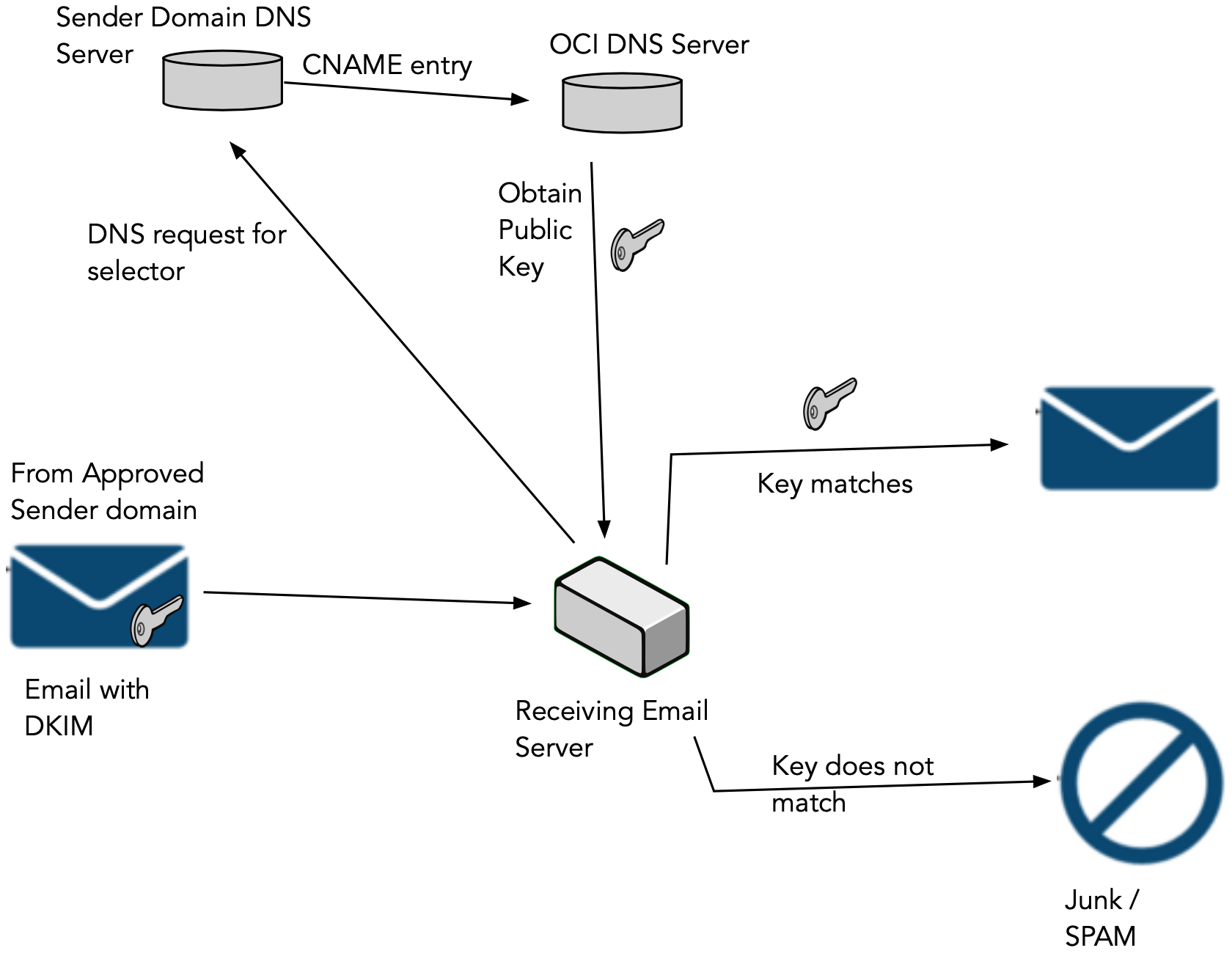
When a network administrator of an organization keeps the DKIM key unchanged for a long time, a threat actor who gets illegal access to the database can steal it. There is an additional security practice that prevents data theft called ‘storage encryption’. But if somehow the cybercriminal gets access to the DKIM key, then it’s just a matter of time before the whole email domain server is compromised. This element is referred to as “vulnerability” in DKIM.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
As a resolution measure, an organization must carry out the action of DKIM key rotation to make sure that their domain is not vulnerable. Along with that, it also makes sure that signatures are updated, enhancing the deliverability rate of emails.
It is extremely important to rotate DKIM keys as it is the first step to mitigating risks on the DNS. It incorporates best practices of cybersecurity awareness and implementation, primarily focused on enhancing email security and defense against attacks on the domain servers.
Regular key rotation practice can reduce the risk of compromise of active public keys. The threat actors can get access to the keys during a data breach. Key Rotation will eradicate the possibility of stolen keys being used by cyber attackers.
There are multiple aspects and methods of rotating DKIM keys. So, there are primarily two aspects – automated and manual. The notion of setting DKIM is to make sure that the public key of the domain and private keys of each mail are appropriately paired. So, setting the DKIM key is the most important element and it must be done carefully. Read more about how to configure DKIM using best practices to avoid any mistakes.
Let us discuss possible and effective methods of key rotation.
Methods of Key Rotation
The process of key rotation involves the allocation of public keys on the DNS of a particular domain. This public key is then paired with a private key which is specific to the sender’s email. This is commonly known as digitally signing the emails and email service provider.
The most simple method of carrying out the key rotation is manual, where a user has to change the public manually and then paste it into DNS. There are some disadvantages to this method, which are discussed in the next section.
CNAME
CNAME refers to a canonical name that is stored in the form of a record, where one domain is mapped with another. So, sometimes an organization’s administrator delegates a vendor to use CNAME. The CNAMEs are under the control of a particular vendor. It means if domain owners need to remove an authorization, then they simply remove CNAME.
The main disadvantage of using CNAME-based delegation is that there is a possibility of allocating multiple DKIM keys, where each of them is based on a particular CNAME. The vendor has the responsibility to rotate that particular DKIM key through that CNAME. When configured, the vendor has the authority to rotate keys without even notifying the domain owner. And this becomes disadvantageous and in some cases problematic for email domain owners.
Subdomain Delegation
Subdomain delegation is the simplest method of key rotation for organizations or domain owners. In this method, an external vendor is hired for handling the responsibility of DKIM key management. The domain owners do not handle DKIM themselves, and rather assign a dedicated subdomain, which sends emails on the behalf of the domain.
The vendor assigned by the domain owners also handles the responsibility of key rotation. Although, the domain owner can take back the administration whenever they want and the vendor will no longer be allowed to carry out DKIM management.
Manual Process of Rotation Should be Avoided
The process of key generation manually requires a tool, then that key is manually copied and pasted into DNS. So, there is a possibility that mishandling or error can occur. That’s why the manual process is disregarded for setting DKIM or specifically key pair.
Automatic DKIM Key Rotation
The email service provider can provide the facility of automatic key rotation, which saves additional time for troubleshooting and fixing the errors. There are some email marketing companies that provide email securing services.
What are the Best Practices for DKIM Key Rotation?
The process of DKIM key rotation, in general, is highly beneficial but there are some practices that must be carried out by domain owners to ensure that it is carried out efficiently. They are listed below.
- Length of Key: The length of the public key should be at least 1024-bit as a shorter key is more vulnerable.
- Expiration Time: Every DKIM signature must have an expiration time that should be greater than the rotation time.
- Rotation Frequency: Every DKIM key must be rotated within a year in general. Additionally, based on the risks involved and the feasibility of the organization, its frequency should increase.
- Test: For a shorter period, the “t=y” tag pair should be used for testing the emails with the DKIM signature.
- Monitoring: In addition to DKIM, DMARC policy should be implemented to monitor whether the emails are signed or not. For that DMARC policy should be set to “p=none”.
How Frequently Should DKIM Key Rotation Take Place?
The choice of frequency for key rotation depends on the extent of the business. Every business has its own risk level according to which it administers its activities for network and domain security.
Generally, it is advised to rotate DKIM keys three to four times a year. One can also choose a higher frequency of rotation. For financial and banking institutions, DKIM key rotation should be carried out on a monthly basis.
The notion of frequency is also dependent on the complexities of the email programs or servers. Some organizations that belong to financial institutions can also choose to decrease the frequency of key rotation because of the complexities of the organization’s domain server.
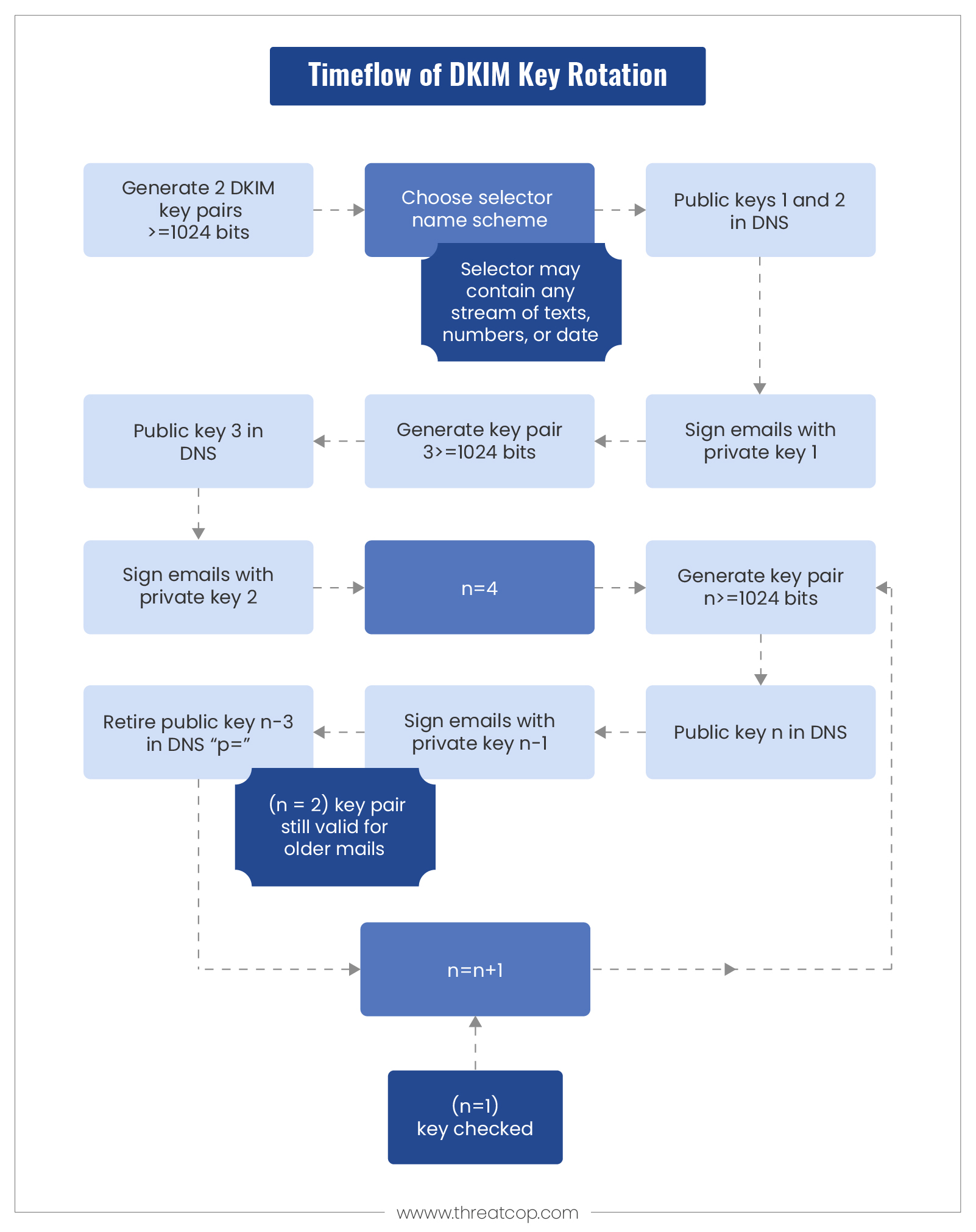
Timeflow of Key Rotation
There are two formats of the public key- 1024-bit and 2048-bit. Initially, at least a 1024-bit public key is allocated to a domain. Then, a selector is used to identify the key and two separate public-private key pairs are defined. The two public parts of the pairs (namely, Public Key1 and Public Key2) are updated in the DNS.
After initially implementing DKIM, the emails are signed using private key 1. After a certain period (which can be 3 or 4 months based on the policy of the organization), key rotation takes place. At first, another public key is generated (Public Key3) and stored in DNS. Then, all the emails are signed with private key 2.
Similarly, generalizing the above process at nth key. Let’s say, at the time of key rotation, a key pair is generated of at least 1024-bit for the nth designation. A public key of Key(n) is stored at DNS. At this point, all the emails are signed using a private key of (n-1)th designation. Then, the public key of (n-3)th designation is discarded from the DNS and the public-private key pair (n-2) will be valid for older emails. This rotation process keeps repeating for every n = n+1.
For more clarification, consider the following image.
Proactive Practices to Ensure Email Security
DKIM is an essential email authentication protocol that works alongside SPF to enhance email domain security. DMARC is an authentication standard that helps implement policies to assist SPF and DKIM. TDMARC is a tool, whose primary purpose is to help domain owners monitor SPF, DKIM, and DMARC configuration. Using this tool, you can keep an eye on the validity of your domain’s DKIM record and check whether or not it’s in proper working order.
Editor’s Note: This post was originally published in February 12, 2022 and has been partially revamped and updated for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Senior Writer
Shantanu is an accomplished content strategist and technology enthusiast at Threatcop Inc. With a knack for translating technical intricacies into reader-friendly narratives, Shantanu contributes to making cybersecurity insights both informative and enjoyable for tech enthusiasts and general audiences alike.
Senior Writer Shantanu is an accomplished content strategist and technology enthusiast at Threatcop Inc. With a knack for translating technical intricacies into reader-friendly narratives, Shantanu contributes to making cybersecurity insights both informative and enjoyable for tech enthusiasts and general audiences alike.
