Cybercriminals are changing, but how they exploit us is not. Hackers still rely on humans. In fact, in the 2023 Data Breach report from Verizon, the human element was present in 74% of breaches. Most hackers will use a technique called baiting. Baiting is a type of social engineering that uses a user’s curiosity, greed or urgency against them.
Table of Contents
ToggleIn this blog, we’ll explore what baiting means in cybersecurity, how it works, what baiting attacks typically look like, and how your organization can effectively protect against them.
What is Baiting in Cybersecurity?
Baiting is a form of social engineering that compels users to install malware or extract sensitive information by luring users in with an offer of free software, gifts or even just cash. Baiting uses either a natural curiosity or greed, and a disdain for almost everything like credit card debt or car payments, ultimately capitalizing on the human element being the most challenging barrier we face in ad hoc cyber defense attempts.
How Does Baiting Work in Cybersecurity?
Baiting is a cyberattack that plays on human curiosity and relies on enticing offers that will convince victims to engage in an act that results in malware infection or data theft.
The core mechanism of baiting: Offer → Action → Compromised
Offer: The attacker makes an offer for something interesting such as a free movie you’ve been wanting to watch, gift cards for taking two minutes to fill out a survey, or a USB drive labeled salary information left by a disreputable colleague, highlighting the hidden risk of USB drives often used in baiting attacks.
Action: The curious victim clicks the link, opens the file or plugs in the USB because they are curious and they want.
Compromise: The victim’s malware is installed, or credentials are stolen, or the attacker gains unauthorised access to sensitive systems/ data.
Visual Flowchart: Baiting Attack Flow
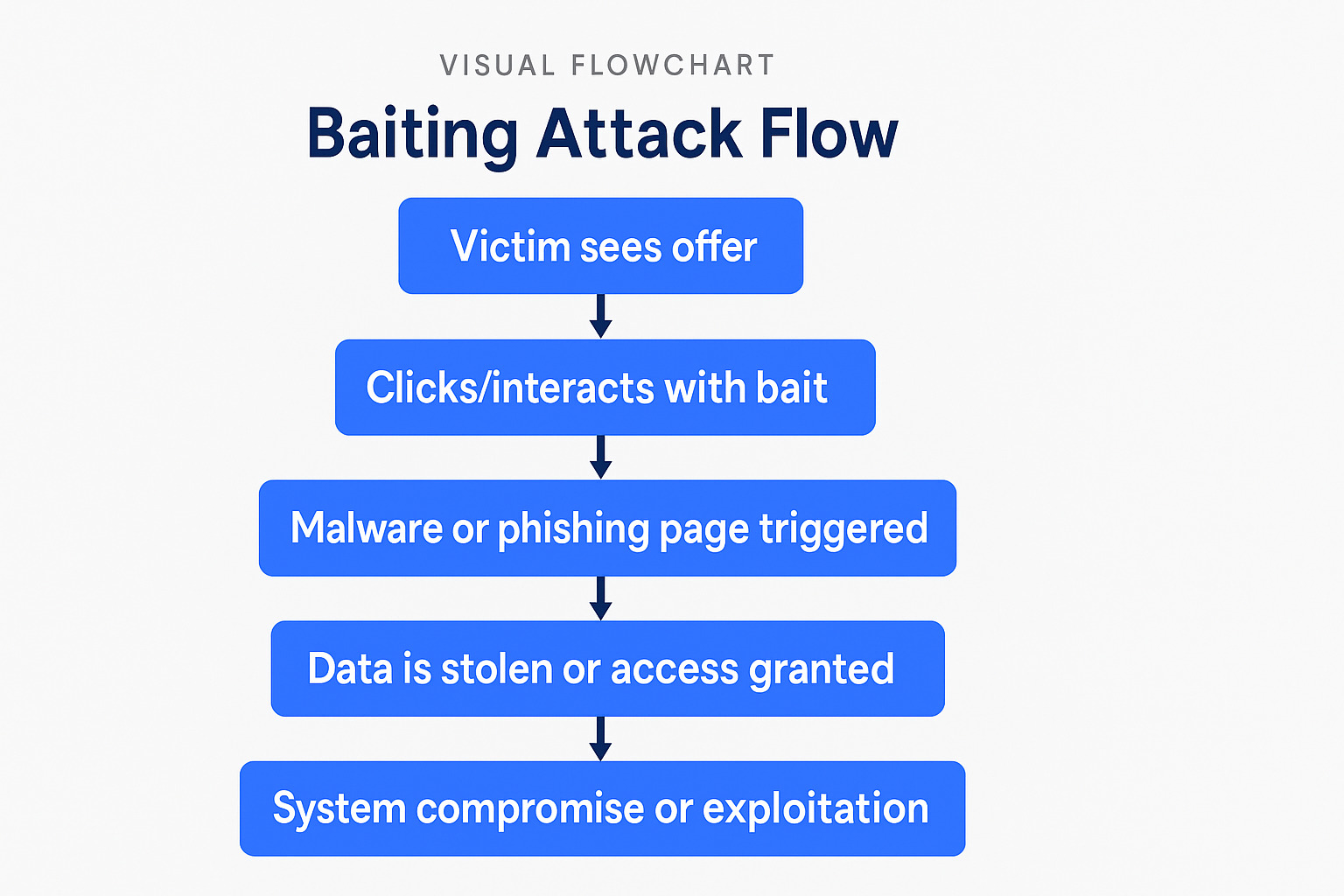
This step-by-step breakdown shows how quickly and subtly a baiting attack can succeed, especially when the victim doesn’t recognize the threat in time.
Psychological Tricks Behind Baiting
Baiting attacks work because they don’t require sophisticated code–they just rely on you. Here are the three most common psychological triggers they use:
- Urgency: “Only 5 gift cards remaining. Claim immediately!” Creates time pressure in order to take you out of critical thinking.
- Scarcity: Limited-time downloads or exclusive offers exploit your fear of missing out (FOMO).
- Social Proof: Fake reviews or testimonials (e.g., “Thousands have claimed their prize!”). It depends on making the offer seem real and legitimate.
Baiting typically follows this pattern:
- An enticing offer is presented.
- The victim takes an action (e.g., clicks a link, plugs in a USB).
- Malware is installed or credentials are harvested.
- The attacker gains access or control.
Psychological triggers like scarcity, urgency, and too-good-to-be-true offers are often used to bypass logical thinking.
Common Types of Baiting Attacks
- Malvertising: Fraudulent advertisements which lead to malicious downloads.
- Physical Baiting: USBs or QR codes that have been infected and left in public places.
- Online Baiting: “Free” movie downloads or software which contain malware.
- Spear Baiting: Target bait from internal company information.
- Email/SMS Baiting: Emails or texts that encourage unsuspecting victims to claim rewards or gift cards.
Real-World Baiting Examples
- Government CD Attack (2018): Malware-loaded CDs were mailed to U.S. state agencies.
- Google USB Experiment (2016): 297 USBs were dropped on a university campus, and 48% were plugged in by unsuspecting users.
- 2023 Gone Phishing Tournament: Found that 1 in 10 employees fell for a phishing bait.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
How to Prevent Baiting Attacks?
Cybersecurity Awareness Training for Employees
Being educated is the best and most effective protection. Employees should be trained to identify baiting attacks and think twice before clicking on unfamiliar links or inserting unknown devices.
Conduct Simulated Baiting Attacks
Simulations are a critical way to evaluate how employees respond to threats. Threatcop’s platform enables organizations to run real-time simulations of baiting and phishing attempts, helping identify user vulnerabilities and continuously measure the effectiveness of security awareness training.
Create a Cyber Aware Culture
While training is clearly critical, organizations should develop policies that shape employees’ behaviour regarding devices (and what equipment is allowed – banning the use of unapproved USB devices) and encourage a speak-up culture that encourages reporting of suspicious incidents.
Put Technical Controls In Place
While baiting attacks target people, technical controls, while not essential, do provide a strong safety net. Building filters into emails, implementing antivirus software and domain protection all may assist in preventing the execution of baiting attacks. Use Threatcop’s TDMARC to ensure your domain won’t be spoofed – an effective way to prevent attackers from using your brand as bait in attacks.
Conclusion
Baiting in cybersecurity continues to be one of the most misleading and harmful forms of social engineering using human behavior. We as human beings are often susceptible to such types of deception and often baiting can succeed even if technology does not aid us. Baiting could be taken away totally if organizations had a proper mix of awareness to their staff, simulations and technical protections.
With this in mind, Threatcop offers organizations the ability to assess, defeat, and demonstrate baiting attacks, assisting your team in handling potential threats effectively. By leveraging Threatcop’s People Security Management AAPE framework (Assess, Aware, Protect, and Empower), organizations can build a structured approach to human risk management. Investing in smarter training and robust policies today creates a powerful defense for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Baiting is a type of cyber attack in which hackers trick victims by baiting them with free or rewarding offers, then trick them into downloading malware onto their systems or giving away their private information.
Baiting is often predicated upon curiosity and/or greed, while phishing is predicated on fear, urgency, and impersonation.
Fake “free iPhone” offers, USB drives that are preloaded with malware, or fake gift card emails offering a free gift after the user inputs their credentials.
