In today’s digital age, the world is constantly under threat from hackers, one such group has earned its place in the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s (FBI) list of ‘Most Wanted.’ The FBI lists China-backed APT41 or HOODOO among the ‘most wanted’ cybercriminals. This group is responsible for various cyber attacks, from stealing sensitive corporate information to conducting espionage operations against governments and organizations worldwide. Recently, APT41 made headlines again by exploiting Google’s Red Teaming Tool, a powerful platform designed to help companies assess their security vulnerabilities.
Table of Contents
ToggleSubscribe to Our Newsletter On Linkedin
Sign up to Stay Tuned with the Latest Cyber Security News and Updates
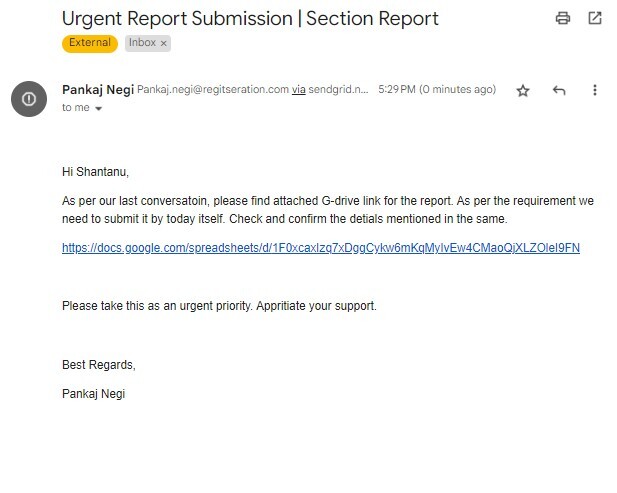
APT41, also known as BARIUM, Winnti, and Bronze Atla, is notorious for actively employing phishing attacks to deceive victims into opening malicious emails. Google’s Red Teaming Tool called “Google Command and Control” (GC2) was designed by Google to help organizations test their defenses against cyberattacks, but APT41 managed to use it as an entry point for conducting sophisticated attacks on several high-profile targets worldwide. In this blog post, we will delve deeper into the methods used by APT41. They attempted to infiltrate an Italian job search company and Taiwanese media organizations by including malicious links to a password-protected file hosted in Google Drive.
Book a Free Demo Call with Our People Security Expert
Enter your details
How APT41 Abused Google Command & Control (GC2)?
Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) revealed that Chinese hackers APT41 are abusing the Google Command and Control (GC2) red teaming tool as they are attacking organizations worldwide. A cybersecurity company is tracking the activities of APT41 since 2014, has claimed that this group of hackers is associated with a famous Chinses hackers group like BARIUM and Winnti.

Let’s understand the tricks and tools employed by APT41 to implement the phishing attack on a Taiwanese media organization.
Breakdown of the APT41 Attack
- During October 2022, TAG claimed that it disrupted a campaign by HOODOO, a Chinese government-backed attacker known as APT41.
- Applying the spear phishing method, the attacker lures the employees of the Taiwanese media organization to download a malicious code file.
- The email provided links to a password-protected Google Drive file that contained the open-source GC2 tool, which was created in the Go programming language and gives attackers access to read commands from Google Sheets and exfiltrate data using the cloud storage service.
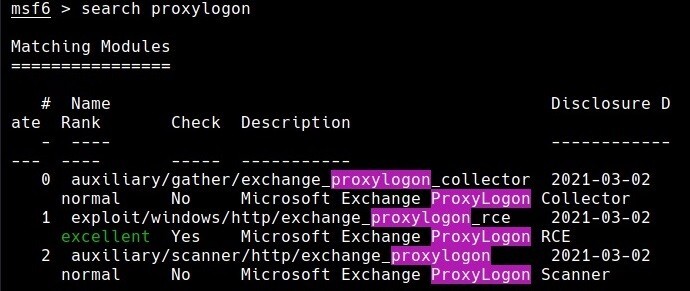
- After installation on the victim’s computer, the malware actively searches Google Sheets for commands from the attacker.
- Apart from using Google Drive for exfiltration purposes, APT41 leverages GC2 to download additional files from Drive onto compromised systems leading to exposure to the victim’s data.
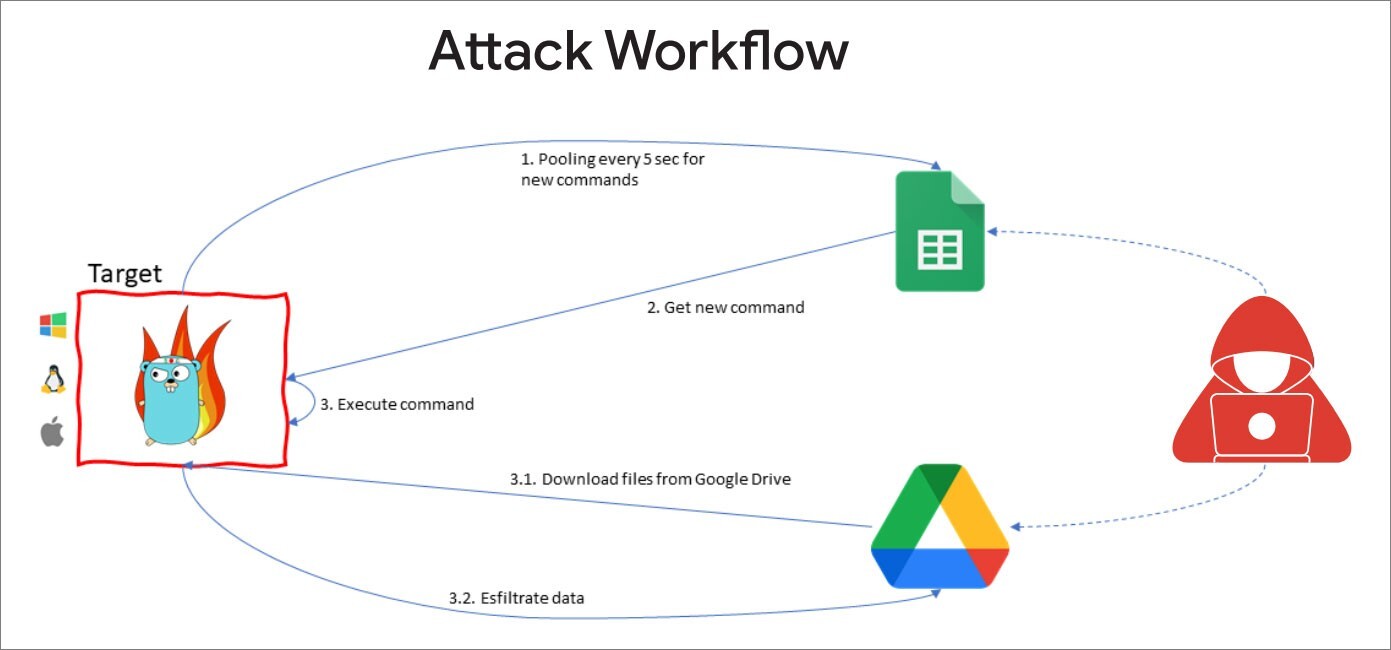
The APT41 launched the same kind of attack in July 2022 to target an Italian job search website utilizing the same malware. Such attacks make it more difficult to find out the attacker as they are using publicly available tools. The program was specifically designed to function as a command and control tool without the need for complex setups like custom domains, VPS, or CDNs during Red Teaming activities. Additionally, the program strictly interacts with Google’s domains (*.google.com) to increase the detection challenge. This information is available in the project’s GitHub repository.
Check Out: Breakdown on Coinbase Data Breach
Who is APT41 Hacker Group?
APT41, often referred to by its infamous code names Double Dragon, Wicked Panda, Wicked Spider, TG-2633, Bronze Atlas, Red Kelpie, and Blackfly, is a well-known advanced persistent threat group that is thought to have connections to the Chinese Ministry of State Security (MSS). In September 2020, the US Department of Justice identified the group in connection with accusations against five Chinese and two Malaysian individuals. The allegations stated that the group had allegedly hacked over 100 companies worldwide. Several cybersecurity firms in 2019 claimed that Double Dragon operated for financial gain and received support from the Chinese Communist Party (CCP).
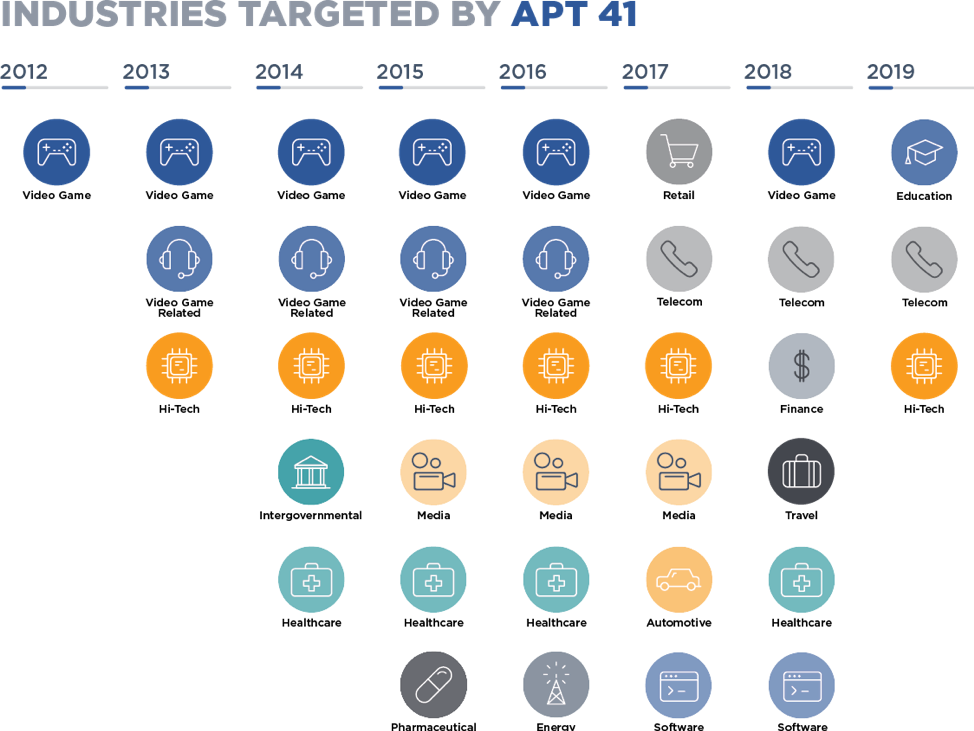
The “Double Dragon,” refers to APT41’s dual focus on espionage and individual financial gain. They predominantly utilize devices typically associated with state-sponsored intelligence activities. Investigations have revealed that APT41 operates across various sectors, including telecommunications, healthcare, and technology. The group extensively conducts financial activities within the video game industry, targeting distributors, development studios, and publishers. A total number of 14 countries were targeted, including India, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States, Switzerland, Singapore, South Korea, France, Myanmar, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Thailand, and South Africa, among the numerous nations.
FBI Listed APT41 on ‘Most Wanted’ List
The U.S. government announced charges on September 16, 2020, against two Malaysian hackers, five alleged participants in a Chinese state-sponsored cyber ring, and more than 100 other businesses worldwide. The group initiated its first attack in 2012. Since then, it has conducted financially motivated operations against the online gaming sector. Additionally, the group has gathered strategic intelligence from significant targets across various industries.
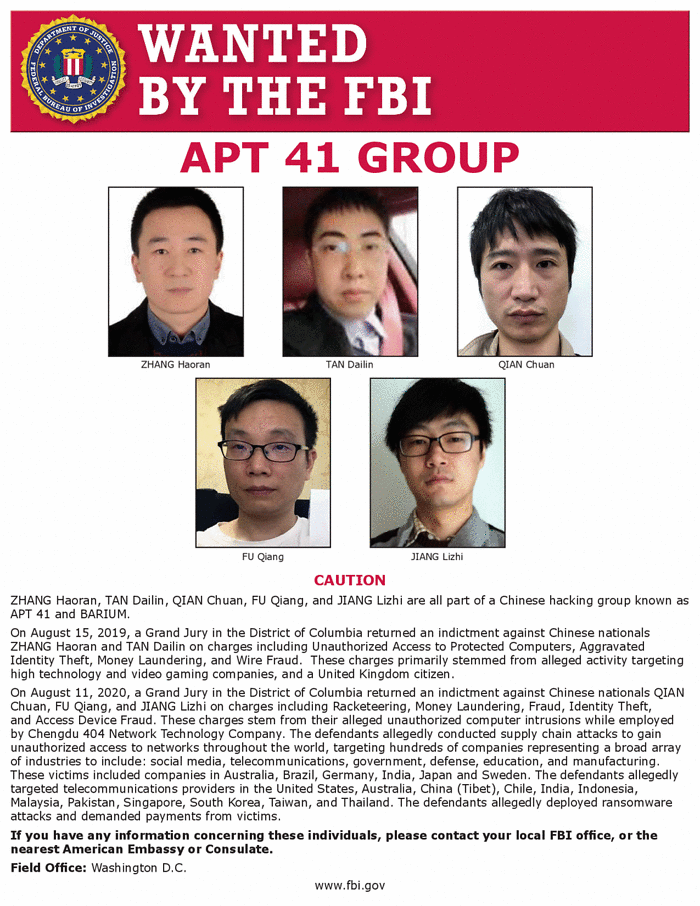
Two of the Chinese hackers, Zhang Haoran and Tan Dailin, were accused in August 2019, according to a news statement from the U.S. Justice Department. The other three hackers, Jiang Lizhi, Qian Chuan, and Fu Qiang, as well as two Malaysian co-conspirators, were indicted separately in August 2020. The three Chinese hackers who were later charged have connections to Chengdu 404 Network Technology. This network security firm operated as a front for the People’s Republic of China.
APT41’s Attacks Throw Light on New Patterns Posed by Threat Actors
Utilization of Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) Tools
Ransomware groups have increasingly started exploiting legitimate remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools, including Action1, to establish persistence on compromised networks and carry out commands, scripts, and binaries. Threat actors can misuse any tool designed for red team exercises or network administration, highlighting an alarming truth. These tools become instrumental in facilitating their malicious attacks.
Weaponizing Publicly Available Tools
The recent development holds significance for two key reasons. Firstly, it indicates a growing trend among Chinese threat groups to utilize publicly accessible tools such as Cobalt Strike and GC2 in order to complicate efforts aimed at attribution. The strategic shift in tactics aims to complicate the identification of the trustworthy source behind cyber attacks.
This observation was backed by the “Threat Horizons Report April 2023” and revealed that threat actors increasingly leverage legitimate red teaming tools and remote monitoring and management (RMM) platforms to evade detection. Threat actors adopt commonly used tools. They can blend in with legitimate network activities, making it challenging for defenders to distinguish between malicious and benign actions.
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) Applied by APT 41
The Chinese group utilizes techniques that are difficult to detect and identify. APT 41 actively employs these techniques in its financially motivated activities, which encompass software supply-chain compromises. Through this method, they are able to inject code into legitimate files for distribution, posing a threat to other organizations by stealing data and manipulating systems. They often rely on sophisticated malware to extract data without being detected. The group also employs boot kits, a type of malware that is challenging to identify and locate among other cyberespionage and cybercrime organizations.
This complexity makes it more difficult for security systems to identify malicious code. Furthermore, they have utilized the Lowkey malware and the Deadeye launcher to conduct immediate reconnaissance while evading detection. APT41 frequently employs spear-phishing emails for both cyberespionage and financial attacks. To increase their chances of success, the organization has sent deceptive emails requesting information from high-level targets, using acquired personal information. Their targets have included bitcoin exchanges for financial gain and media organizations for espionage purposes.
Softwares used by APT41 Hacker Group
APT 41, as reported by the Department of Health and Human Services of the United States, utilizes various software tools for malicious activities. These tools include:
- BLACK COFFEE– A versatile tool capable of acting as a reverse shell, aiding in enumeration and deletion, as well as facilitating command and control (C2) communications while employing obfuscation techniques.
- China Chopper– A web shell designed to grant unauthorized access to enterprise networks, allowing the attackers to infiltrate and operate within the targeted systems.
- Cobalt Strike– A commercially available tool frequently employed by attackers to deploy and execute malicious payloads, enabling them to carry out their intended actions.
- Gh0st Rat– A remote access tool (RAT) utilized by APT 41 to gain unauthorized control over compromised systems and establish continued access for subsequent malicious activities.
- Mimikatz– A credential dumping tool employed by the group to extract plain-text Windows account information, aiding them in obtaining sensitive credentials for further exploitation.
- PlugX– A RAT equipped with modular plugins, offering APT 41 additional capabilities to exploit and control compromised systems as per their specific requirements.
- ShadowPad- A modular backdoor commonly utilized by APT 41 for command and control communication, providing them with a means to remotely control compromised systems and carry out malicious activities.
Significance of Employee Vigilance in the Era of Cloud Services
Stressing the value of employee awareness is crucial in the contemporary cloud services ecosystem. Organizations may improve their security posture and secure priceless assets by increasing employee awareness. With the popularity of cloud-based services, fraudsters are using spear phishing attacks and other social engineering techniques to exploit these systems’ flaws. For instance, current data indicates a 400% increase in credential-stuffing attacks over the previous year. Consider the following key points to safeguard your eco-system:
Protection from Phishing Attacks
When handling emails, employees need to be watchful and cautious to avoid falling for phishing scams that try to deceive them into disclosing personal information or clicking on hazardous links.
Protecting Sensitive Data
When using cloud services, employees must be aware of the significance of handling and safeguarding sensitive data appropriately. This includes using strong passwords, avoiding sharing login information, and adhering to secure file-sharing procedures.
Awareness of Social Engineering Tactics
Organizations should actively inform employees about common social engineering techniques employed by attackers, such as impersonation or manipulation. These techniques exploit employees’ confidence, tricking them into divulging sensitive information.
Detecting Suspicious Activity
It’s important for staff members to be able to see suspicious activity in cloud services, such as unauthorized access attempts, irregular file sharing or deletion, or unexpected system behaviors, and to report any issues as soon as they arise.
Regular Security Awareness Training
The organization should regularly conduct security training to ensure staff members are aware of new risks, best practices for cloud security, and the company’s policies and procedures for using the cloud and protecting data.
Organizations can considerably improve their entire security posture to reduce risks and guarantee the safe and responsible use of cloud technology. According to a recent survey, 78% of customers would cease doing business with a company if their data was hacked. So, employee education aims to avoid cyberattacks while also preserving stakeholder and customer confidence.
To mark Cybersecurity Awareness Month, Threatcop collaborated with 31 respected CISOs and CTOs from prominent organizations. Together, we’re working towards a safer digital future.
Explore Here: 31 Cybersecurity Awareness Ideas from Security Leaders
FAQs: APT41 exploiting Google’s Red Teaming Tool
Spear phishing attacks are a type of targeted cyberattack in which the attacker targets particular people or groups with nefarious emails or other forms of communication. Spear phishing is more personalized than general phishing assaults and frequently appears to be from a known or trusted source, such as a coworker, business partner, or even a friend. The purpose of spear phishing is to deceive the target into performing actions that may compromise their security, such as clicking on a malicious link, downloading a file that contains malware, or disclosing private information like login credentials.
In a phishing campaign, hackers attempt to trick victims into revealing private information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, or other sensitive data. In phishing campaigns, attackers usually use methods like urgent demands, fear tactics, or attractive offers to compel victims to take action. Phishing attempts try to get people to give up their personal information so the attackers can use it.
A red teaming tool is a piece of software or a collection of tactics used to mimic actual cyberattacks on an organization’s infrastructure, networks, and systems. Red teaming is used to evaluate an organization’s security posture by spotting flaws, gaps, and potential security exploits that would be useful to hackers.
Using red teaming technologies, it is possible to simulate the tactics, methods, and procedures (TTPs) used by genuine cyber attacks. Various attack scenarios, including social engineering, network infiltration, web application vulnerabilities, and others, can be simulated using these tools. They assist organizations in assessing their resistance to advanced cyber threats, incident response protocols, and defense capabilities.
Hacker organizations work by utilizing the knowledge of their members and using a variety of tactics to access computer systems and networks. They use secure channels to communicate, find weak points in their targets, and take advantage of those points by utilizing malware, hacking tools, or social engineering. However, it’s vital to remember that their actions are illegal and present serious hazards to people and organizations, regardless of their motivations, which might range from financial gain to activism.
The most notorious hacker group in the world is allegedly Anonymous. Anonymous is a group of international hackers and activists known for their high-profile cyberattacks and protests. To advance causes, expose corruption, or promote internet freedom, they have attacked a variety of governmental entities, businesses, and organizations. They are now among the most well-known and contentious hacking organizations worldwide as a result of their operations, which attracted considerable media attention.
The phrase “Living off the Land” (LOTL) is a hacking strategy in which hackers use legitimate tools and features already present on a hacked system to conduct their operations, making it more difficult to identify their malicious behavior. This strategy has been used by APT41, a hacker group linked to China.
An open-source Go project called GC2, commonly referred to as Google Command and Control, was created for use by red teams. This program was created to offer command and control during red teaming activities without requiring a specific setup (such as a custom domain, VPS, CDN, etc.).To further complicate discovery, the program will only communicate with *.google.com domains owned by Google.
APT41 targeted the Taiwanese media organization by sending phishing emails that contained links to a password-protected file hosted in Drive. The payload was an open-source red teaming tool called “Google Command and Control” (GC2). The campaign was disrupted by Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG).
Employee awareness is crucial to averting phishing attempts because it equips workers to identify and steer clear of the misleading strategies utilized by hackers. Employees can lessen their risk of becoming a victim of phishing attacks by recognizing the telltale signs of these assaults in emails, links, and requests by being aware of the features of phishing attempts. Their awareness contributes to the protection of confidential data, the preservation of corporate assets, and the reduction of phishing-related financial losses.